What kind of instructions are there? The main types of instruction at the enterprise and their brief description. Types of instruction
When applying for a job at any enterprise, regardless of whether it is engaged in the manufacture of something dangerous or an educational institution, each employee must receive instructions on labor protection.
There are several of them, they must be carried out by a trained and responsible person, the results are documented. We will help you figure out what they are, what they should tell workers about, and how to register them.
If you understand the issue, What is training and why is it needed?, it is worth noting that this training is for those who have just come to work and those who have been working here for a long time.
It is believed that Newly-minted specialists require special attention. The purpose of this information for them is to convey maximum information regarding what is happening at the enterprise, how to avoid injuries, damage, and troubles during the work process that may arise due to inexperience.
Also people with great experience must regularly listen to amendments, because sometimes they are very confident in their knowledge, which leads to injuries and violations of safety regulations.
The main goal of any instruction is to train workers in labor rules, basic positions, and how to avoid accidents at one or another stage of activity.
Besides, instructions are one of the main ways to test knowledge. After the lesson has passed and all the information has been transmitted, an exam is conducted, during which the level of knowledge is determined. If the test is not passed, then there are grounds either for further course or for suspension from work for some time.
What types are provided, main provisions and differences
Carrying out Instructions in production are carried out more than once. Based on the nature and time of implementation, the following types of labor safety briefings are divided:
Let us briefly consider what types of briefings there are on occupational health and safety in the workplace at an enterprise.
Introductory. The first instruction all new arrivals must listen. Even if the worker has extensive experience in the past, this is his first time at this enterprise, so this cannot be avoided. It is also listened to by trainees, business travelers, and temporary people.
The main goal is to familiarize yourself with the rules at the enterprise, in workshops educational institution, at landfills. Familiarization is made with benefits and compensation, with the main provisions of the law, first aid, means of preventing fire, and rules of action in emergency situations.

Primary. When a person was hired for production, before starting the activity, he must listen to this type of introduction. It is also auditioned by those who are transferred to other jobs, or are expected to do something new for themselves. But some employees who do not deal with:
- Tests;
- Repair equipment;
- Using tools;
- The use of raw materials or materials for production.
This list must be approved by the production manager, and it is approved by the union. After this, an internship with a supervisor who has more experience and can control the entire process is required.
Repeated. It pursues almost the same goals as the primary one. It is carried out according to the same program. Employees who were exempt from the primary are exempt from it. It is carried out once every 6 months or less. The boss has the right to set his own deadlines.
Unscheduled. The name alone speaks for itself. They are carried out in unforeseen situations. For example:
- When new means or materials are introduced into production;
- When changing equipment;
- When someone violates safety regulations;
- When required by supervisory authorities.
Depending on the reason for which it is carried out, the program and volume are determined.
Target. A certain period is allotted for this type, and it is carried out only for a specific purpose, for example:
- Performing one-time work that is completely different from the main duties;
- Elimination of consequences of the accident;
- When carrying out work for which additional documentation, work orders, etc. are issued.
Who can conduct
 If there is no position of occupational safety engineer, then familiarize yourself with the head of the enterprise can give the rules and specifics(for example, this applies to educational institutions or sports complexes).
If there is no position of occupational safety engineer, then familiarize yourself with the head of the enterprise can give the rules and specifics(for example, this applies to educational institutions or sports complexes).
These people are responsible not only for carrying out, but also for the further implementation of instructions by the employee. They also record record all data in the appropriate log.
Those who are just entering the enterprise are instructed(introductory, initial briefings), workers with extensive experience, to refresh their knowledge in order to avoid tragedies. Also, those who work temporarily, or people who are transferred to other facilities or assigned to other machines or equipment, should also undergo a brief briefing on labor safety.
That is, any new responsibility must be previously covered. All rules, requirements and warnings are submitted. It also talks about the employee’s responsibilities and describes his actions in certain situations.
Registration procedure, main program, rules and instructions for conducting
Any training and instructions on labor protection must be documented. The same goes for instructions. Of course, when the class itself is taught, an attendance register is kept, unless it is a one-time course. At the end of this type, a note is made in the journal that the employee has completed it and has certain knowledge.
Depending on production, the employee may be given a job assignment. If it does not contain a mark on completion of the training, then the production manager does not have the right to allow such a person to work.
The program for which instruction is carried out is dictated by the legislation regarding a particular production. At the end, a survey, test or exam must be conducted that will prove the employee’s knowledge and provide him with admission.
Instructions at any level are usually carried out according to the following rules:
- In a group or individually (water is usually individual, since several people are rarely received at the same time, but the primary and the rest are most often group classes).
- Training is conducted as a conversation.
- The duration of the conversation is at least one and a half hours.
- Demonstration of equipment and materials is required.
- It is possible to use visual videos or photographs that demonstrate accidents associated with non-compliance with safety regulations.
Instruction is important stage in production. Each of them has its own goals that need to be achieved during training. Correctly drawn up instructions are a guarantee of safe work at any enterprise.
To combat industrial injuries in shops and workshops of an enterprise, it is necessary to conduct the following types of induction training: introductory, primary at the workplace, periodic and unscheduled.
Photo
Characteristics
Induction training
Introductory training is carried out with all newly hired employees, regardless of their education, work experience in a given profession or position, as well as with posted workers, students, students arriving for on-the-job training or internship. 
Initial training at the workplace must be carried out with all newly hired employees transferred from one department legal entity to another, business travelers, schoolchildren and students, as well as with employees who are entrusted with performing work that is new to them. This type of instruction is carried out with each employee individually with a demonstration of safe work practices.
Re-briefing is carried out with the aim of testing and increasing the employee’s level of knowledge of labor protection rules and instructions individually or with a group of workers of the same profession or team under an on-the-job training program.
With your own hands
Financing occupational safety
Financing of preventive measures on labor protection, implementation of national, sectoral and regional programs to improve the state of safety, occupational health and working environment, etc. government programs, aimed at preventing accidents and occupational diseases, is carried out by the state and local budget, along with other sources of funding.
For enterprises, regardless of their form of ownership, or individuals who use hired labor, labor protection costs are set at no less than 0.5% of the amount of products sold. In enterprises that are maintained at the expense of the budget, labor protection costs are provided for in the state or local budget and amount to at least 0.2 percent of the wage fund.
Labor protection funds: - state - under Gospromgornadzor; -industrial - under ministries, other central government bodies executive power, associations of state enterprises performing the functions of managing the property of these enterprises; - regional - in the Republic of Crimea, regions, cities of Kyiv and Sevastopol, districts, with the exception of districts in cities; - enterprises - at self-supporting enterprises, regardless of their form of ownership.
The management of the state labor protection fund is carried out by Gospromgornadzor, which:
* accumulates funds coming from various sources and directs them to solve problems in the most priority areas labor protection, to ensure implementation public policy Ukraine in this area;
* compiles cost calculations for the implementation of specific labor protection measures;
* provides financing national program improving the safety, health and working environment;
* exercises control over the correct and efficient expenditure of funds, as well as their timely and complete receipt in state fund labor protection from enterprises, public organizations and citizens through voluntary contributions.
Article 271. Violation of labor protection legislation: 
1. Violation of the requirements of legislative and other regulatory acts on labor protection by an official of an enterprise, institution, organization or citizen - subject entrepreneurial activity, if this violation caused harm to the health of the victim, is punishable by a fine of up to fifty tax-free minimum incomes, or correctional labor for up to two years, or restriction of freedom for the same period.
2. The same act, if it caused the death of people or other grave consequences, is punishable by correctional labor for a term of up to two years, or restriction of liberty for a term of up to five years, or imprisonment for a term of up to seven years, with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions, or engage in certain activities for a period of up to two years or without it.
Article 272. Violation of safety rules when performing work with increased danger:
1. Violation of safety rules when performing work with increased danger in production or any enterprise by a person who is obliged to comply with them, if this violation created a threat of death or other grave consequences or caused harm to the health of the victim, is punishable by a fine of up to fifty tax-free minimum incomes citizens or correctional labor for up to two years, with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for up to three years.
2. The same act, if it caused the death of people or other grave consequences, is punishable by restriction of freedom for a term of up to five years or imprisonment for a term of up to eight years, with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years.
Instructions
Types of liability for violation of labor protection rules.
One of the main functions of state and public control is to increase responsibility for labor protection not only of enterprises, but also of all workers. The legislation establishes disciplinary, administrative, financial and criminal liability (Article 44). Disciplinary liability includes reprimand, reprimand, dismissal. Disciplinary liability is imposed on everyone: workers, employees, engineers if they violate labor safety requirements, which could lead to injury or an accident. 
Disciplinary sanctions can be imposed by an official or a higher authority along the line of subordination, and on management employees and on the initiative of trade union bodies. If a managerial employee violates labor legislation or does not fulfill obligations under a collective agreement, then at the request of a trade union body (not lower than a district one), the administration is obliged to remove him from his position or dismiss him. Disciplinary liability cannot be imposed later than six months from the date of violation. After a year disciplinary liability is automatically removed. Administrative responsibility. According to Article 43, for violation of labor protection legislation, failure to comply with orders of officials of state supervision bodies on labor protection, legal entities and individuals who, in accordance with the law, use hired labor, are held administratively liable (payment of a fine in accordance with the procedure established by law). The maximum fine cannot exceed five percent of the monthly fund wages legal entities and individuals. Failure to pay a fine by legal entities and individuals entails a penalty of two percent for each day of delay. The fine is imposed within a month from the date of violation; the fine is collected from the cashier at the place of work.
The decision to impose administrative liability can be appealed in court within a month (the application is submitted to the district (city) people's court). Cash from the application of penalties to legal or individuals are transferred to the state budget of Ukraine. Administrative liability also includes illegal actions or inaction, obstacles in the implementation functional responsibilities officials of state supervision and representatives of trade union bodies (including avoidance of participation of the administration in negotiations on the implementation of the collective agreement and amendments to it).
TO financial liability compensation applies material damage the enterprise for violations of labor protection that resulted in damage. Workers and employees are required to compensate for damages regardless of disciplinary, administrative or criminal liability. The legislation provides for two types of liability: limited and full.
The main type is limited liability within one month tariff rate(salary) of the employee. Directors of enterprises and their deputies bear financial liability in the amount of damage caused, but not more than the average monthly salary. Damage is recovered with the written consent of the employee by order of the enterprise administration; deduction is made in parts from his salary. The retention order is issued no later than two weeks from the date of discovery of the damage.
In the absence of the employee's written consent, compensation for damages is made by decision of the district people's court. The heads of enterprises and their deputies are compensated for damages based on a court decision following a claim from a higher authority or a statement from a prosecutor. The administration is obliged to go to court on the issue of compensation for material damage within a month from the date of discovery, if financial liability is within one third of the salary, and in case of greater material liability - within a year. If there are signs of malicious intent in the employee’s actions, full financial liability or criminal prosecution (by court decision) may be imposed.
An employee is exempt from criminal and financial liability if the harm caused is caused by the need for self-defense or an emergency to avoid accidents and other negative consequences (elimination of a threat to the lives of others). Criminal liability occurs in case of violation of safety precautions, sanitary, fire safety rules and regulations that led to an accident, injury and other negative consequences and is determined by Art. Criminal Code of Ukraine.
The penalty depends on the degree of violation and may include dismissal, a fine of up to 15 minimum sizes wages, correctional labor or imprisonment from 1 to 7 years.

To combat industrial injuries in workshops and workshops of the enterprise, it is necessary to carry out the following types of instruction in production ( enterprise): introductory, primary at the workplace, periodic and unscheduled - this is main types of briefings. Induction training is carried out for all newly hired employees. The administration has no right to allow newcomers to do any work unless they have undergone induction training.
The introductory briefing is carried out by a safety engineer, and the following issues are considered: labor protection in the USSR and the main provisions of Soviet labor legislation; internal labor regulations of the enterprise; safety requirements for special clothing, hats, and safety shoes; electrical safety rules, including issues of freeing the victim from live parts and providing first aid; basic requirements for sanitation and personal hygiene, as well as the procedure for using household premises and public places; the importance of ventilation and rules for using ventilation units; rules of conduct for workers in case of accidents; rules of provision first aid in case of accidents. Everyone who is hired or transferred from one job to another undergoes initial training at the workplace. In addition to instruction, they are trained in safe work practices. 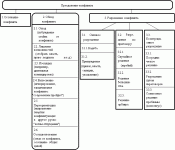
Initial instruction is carried out by the foreman or site manager. The briefing includes the following issues: familiarization with the design and operation of the equipment to be maintained or repaired; familiarization with safety regulations; familiarization with the correct and safe maintenance of the workplace and tools; familiarization with safe work practices. After the initial briefing, it is necessary to organize training in safe work practices over several shifts (up to 8 shifts). Periodic briefing is carried out with all employees, regardless of their qualifications and work experience, on a quarterly basis. The briefing is carried out by the site foreman with the participation of the workshop manager, and the provisions of the instructions are illustrated concrete examples from practice.
The purpose of the instruction is for workers to learn correct and safe work techniques. Unscheduled briefing is carried out in the event of a change in the technological process or replacement of equipment, when labor safety conditions change (when servicing machines or repairing them). Conducting an unscheduled briefing is documented, just like the above, with a corresponding entry in the journal. To ensure labor safety in production workshops, there must be created best conditions for operation and repair of technological equipment. Each worker must have at least 4.5 m2 of production area and at least 15 m3 of room volume.
The floors of premises (workshops, areas) must be durable, non-slip, without holes and thresholds. The equipment is installed in such a way as to create favorable and safe working conditions, simplicity and ease of operation. When arranging equipment, the following factors are taken into account: overall dimensions of the equipment and its design; position of the grid of columns and dimensions of the room; traffic lane; machine maintenance areas; working passages and gaps between machines, columns and walls; evacuation passages.
Correct placement of equipment, including repairs, allows you to rationally organize workplace, ensure labor safety. At the workplace, tools should be placed so that they can be used without unnecessary movements (minimal hand movement). Light signaling devices are installed at the operator’s eye level.
Today we talked about five types of briefings their meaning and concept. Take care of your health!
Procedure for conducting on-the-job training
1.1. This Regulation establishes the procedure for conducting briefings, training, internships and testing knowledge on labor protection in federal railway transport: - workers (students), specialists and managers; - students and pupils who arrived at enterprises, institutions and organizations to undergo industrial training or practice; - persons involved in urgent work to eliminate the consequences of wrecks, accidents, snow drifts, floods and others natural Disasters. The regulations were developed on the basis of GOST 12.0.004 “SSBT. Organization of occupational safety training. General provisions”, as well as regulations of the Ministry of Railways of Russia.
1.2. This Regulation applies to enterprises, institutions and organizations of federal railway transport (hereinafter referred to as enterprises), departments and administrations of the Ministry of Railways of Russia (hereinafter referred to as structural divisions of the Ministry of Railways of Russia). The provision does not apply to the procedure for training and testing knowledge on labor protection of students and students during their training in higher and secondary specialized educational institutions Ministry of Railways of Russia. The procedure for training, instructing and testing knowledge on labor protection of personnel servicing facilities controlled by state and departmental supervision bodies is carried out in accordance with regulatory acts of state supervision. Enterprises must develop and approve local regulations that take into account local specifics of training and testing knowledge on labor protection. 
1.3. Upon admission (transfer) to permanent, temporary or seasonal work, depending on the profession (position), qualifications and type of upcoming labor activity At the enterprise, employees must be provided with: - introductory briefing on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as introductory briefing) (except for persons transferred from one job to another within the enterprise); - initial briefing on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as initial briefing) at the workplace; - training in labor protection during training of workers, retraining and training in second professions; - internship; - initial testing of knowledge on labor protection; - duplication (with operational managers, operational and operational maintenance personnel in the electrification and power supply sector).
1.4. In the process of work, depending on the profession (position), qualifications and type of work activity at the enterprise, employees must be provided with: - repeated instructions on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as repeated instructions); - unscheduled briefing on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as unscheduled briefing); - targeted briefing on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as targeted briefing); - occupational safety training; - periodic and extraordinary testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements.
1.5. All types of briefings and internships must be recorded in the appropriate logbooks for registering labor safety briefings, with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing. Log Forms induction training and on-the-job training are given in Appendices 1 and 2 to these Regulations. The pages of the labor safety briefing logbooks must be bound and numbered. At the end of the journal, the number of numbered pages certified by the signature and seal of the enterprise must be indicated in words. Records of briefings and internships in the logbook for registering briefings on labor protection in the workplace should be kept in chronological order. It is allowed to allocate separate pages for registration of each type of instruction and internship in the logbook for registering instruction on labor protection in the workplace. The list of persons responsible for maintaining and storing logs of labor safety briefings in the divisions of the enterprise is established by order of the enterprise.
1.6. Workers, heads of departments and specialists of enterprises*, heads of departments and specialists of services (directorates), railway management departments, departments of railway departments (branches), who are not subject to testing in knowledge of the Technical Operation Rules railways Russian Federation(hereinafter referred to as PTE), as well as students and apprentices who arrived at the enterprise to undergo industrial training and practice, must undergo a knowledge test on labor protection in the commissions of the enterprise, service (directorate), department (branch) of the railway. The commission for testing knowledge on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as the commission) includes: - the chief engineer, another head of the enterprise or the head of a structural unit of the enterprise, the chief engineer or deputy head of the service (directorate), the railway management department, the department of the railway department (branch) roads (chairman); - labor protection engineer or other specialist entrusted with labor protection responsibilities; - representative of the elected trade union body. The commission may include chief mechanical engineer, Chief Power Engineer, chief technologist, heads of structural divisions and other specialists of the enterprise, service (directorate), department. At enterprises employing more than two thousand people or having structural divisions located more than 3 km from the enterprise, it is allowed to create commissions to test knowledge at production sites, workshops and other large structural divisions of the enterprise. The composition of the commissions for testing knowledge on labor protection of employees of railway stations and other structural units reporting directly to services (directorates), departments (branches) of railways, respectively, includes heads and specialists of services (directorates), departments (branches) of railways. The heads of these railway stations and other structural divisions of enterprises also take part in the work of the commissions. At enterprises that are not part of the power supply system, testing the knowledge of personnel who are granted the right to remotely switch contact network disconnectors and overhead power lines is carried out in a commission, the composition of which must be agreed upon with the head of the power supply distance. Lists of personnel of enterprises must be approved by the head of the department (branch) of the railway, and in the absence of a department (branch) - by the head of the corresponding service (directorate) of the railway. The composition and operating procedures of the commissions are established by the head of the enterprise, service (directorate), department (branch) of the railway.
1.7. Managers and chief specialists of enterprises (chief power engineers, chief mechanics and other chief specialists), who are not subject to testing in knowledge of labor regulations, depending on their subordination, must undergo testing of knowledge on labor protection in higher commissions: - enterprises subordinate directly to the structural unit of the Ministry of Railways of Russia - in commissions under this structural unit; - enterprises within the railway - in a commission under the management of the railway or the corresponding service (directorate), department; - enterprises within a department (branch) of the railway - in the commission of the department (branch) or department of the department of the railway. The composition of these commissions includes: - deputy head of a structural unit of the Ministry of Railways of Russia, chief engineer or deputy head of a railway service (directorate), department (branch) of a railway, which is entrusted with labor protection responsibilities (chairman); - head (specialist) of the labor protection service (department, sector, group) or labor protection engineer; - representative of the relevant elected trade union body; - chief (leading) and other specialists of the structural unit of the Ministry of Railways of Russia, the railway service (directorate), the railway department (branch) that forms the commission. If necessary, representatives of state and departmental supervisory authorities, the federal labor inspectorate, and the Russian Trade Union of Railway Workers and Transport Builders can take part in the work of the commission. The composition and operating procedures of the commissions are established by the heads of structural divisions of the Ministry of Railways of Russia, services (directorates), departments (branches) of the railways. Testing the occupational safety knowledge of managers and chief specialists of enterprises can also be carried out during their training in industry-specific training organizations designated by the Labor Safety Administration of the Ministry of Railways of Russia in agreement with the Ministry of Labor of Russia as industry-specific basic training centers of the Ministry of Railways of Russia (hereinafter referred to as the training centers of the Ministry of Railways of Russia).
1.8. Testing knowledge of labor protection among workers subject to testing in knowledge of PTE, Rules for the operation of consumer electrical installations (hereinafter referred to as PEEP), approved by the State Energy Supervision Authority of Russia on March 31, 1992, rules for the safe operation of facilities controlled by regional boiler inspection inspections of the Ministry of Railways of Russia and other state and departmental supervision bodies , should be carried out simultaneously with testing knowledge of these rules. In the event of an extraordinary test of knowledge on labor protection or a discrepancy between the timing of testing of knowledge on labor protection and the timing of testing of knowledge established by the relevant rules, employees undergo a knowledge test in the commissions specified in paragraphs 1.6 and 1.7 of these Regulations.
1.9. The examination of knowledge on labor protection must be carried out by commissions consisting of at least three people.
1.10. If employees receive an unsatisfactory assessment when testing their knowledge of labor protection, a deadline is assigned re-check knowledge. This period should not exceed one month. Until re-testing knowledge on labor protection, unless otherwise regulated by the relevant rules, workers should not be allowed to independent work, which is subject to additional (increased) labor safety requirements.
1.11. The results of testing knowledge on labor protection must be recorded in the minutes of the meeting of the commission for testing knowledge on labor protection, the form of which is given in Appendix 3 to these Regulations, or in the minutes of another form established by the relevant rules approved by state and departmental supervision bodies. Managers, specialists and workers involved in work that are subject to additional (increased) labor safety requirements who have successfully passed the labor safety knowledge test must be issued certificates in the form given in Appendix 4 to these Regulations, signed by the chairman of the commission, certified seal, or other form of identification established by the relevant rules approved by state and departmental supervisory authorities.
1.12. The procedure for transferring information about the completion of briefings, training, knowledge testing and internships from the personnel department and departments of the enterprise to the labor protection engineer is established in an order or other local normative act enterprises and must be included in the personal card for undergoing briefings, training, internships, testing knowledge on labor protection and access to work (hereinafter referred to as the personal card), the form of which is given in Appendix 6 to these Regulations.
1.13. At enterprises for conducting occupational safety classes, there must be occupational safety rooms, which can be combined with technical study rooms, equipped with technical means of training and knowledge testing. For practical training in safe work practices, simulators, control and training machines, computers with training programs, and training grounds should be used.
1.14. Workers of complex teams, as well as persons combining professions, are trained, instructed, and tested in full knowledge of labor protection, both in the main and in the combined profession (work).
1.15. The organization of briefings, training, internships, testing of knowledge on labor protection and permission to work in the enterprise as a whole rests with the employer or a person authorized by him (hereinafter referred to as the head of the enterprise), and in divisions of the enterprise - with the heads of departments. Monitoring of labor safety training in departments of the enterprise should be carried out by a labor protection engineer or another specialist of the enterprise who is assigned labor protection responsibilities by order of the enterprise.
Types of instruction.
All employees, when hired and during the work process, undergo instruction (training) at the enterprise. Admission to work of persons who have not undergone training, instructions, and knowledge testing on labor protection is prohibited. Responsibility for organizing, training and testing knowledge at the enterprise rests with the manager, and in structural divisions (site, workshop, etc.) - with the heads of these divisions. Monitoring of training and frequency of knowledge testing is carried out by the labor protection service or employees who are assigned these responsibilities by the head of the enterprise.
Based on the nature and timing of briefings, they are divided into: introductory, primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted. Employees are allowed to work independently after introductory training, initial training at the workplace, and internship. Induction training is carried out:
a) with all employees newly hired (permanent, temporary) regardless of their education, work experience in this specialty;
b) with posted workers who take part in production process; with drivers of vehicles entering the enterprise territory for the first time;
c) with students, pupils, pupils who arrived at production for internship, labor and vocational training; Introductory briefing is carried out by a labor protection specialist or a person appointed by order of the enterprise, in the labor protection office or in a specially equipped room. 
The training program is developed by the labor protection service, taking into account the specifics of production. A record of completion of the briefing is made in the introductory briefing journal and in the person’s hiring document. Initial briefing is carried out at the workplace before starting work:
a) with newly hired employees;
b) with employees who are transferred from one workshop (site, construction site) to another;
c) with an employee who will perform a new job for him;
d) with posted workers taking part in the production process;
e) with students or students who arrived for practical training.
The initial briefing program is developed by the head of the workshop or site, agreed with the labor protection service and approved by the head of the enterprise or the corresponding structural unit. The head of the enterprise is obliged to give the employee a copy of the labor protection instructions according to his specialty or place it at the workplace.
After the initial briefing, the worker must undergo an internship during the first 2-15 shifts under the guidance of experienced, qualified specialists appointed by order (instruction) for the workshop, site, or enterprise. Repeated training is carried out for all employees once every six months and for high-risk jobs once a quarter. Instruction is carried out according to the initial instruction program. Unscheduled briefing is carried out:
a) upon the entry into force of new, revised regulations, upon the introduction of amendments and additions to them;
b) when changing the technological process, replacing and modernizing equipment, instruments, tools, raw materials, materials, etc.;
c) in case of violation of regulations;
d) at the request of specialists of the State Supervision Service for Labor Protection or a higher department, executive authorities in case of violation by employees of safe labor practices, regulations, or violations of labor protection requirements;
e) if there is a break in work of more than 30 calendar days - for work with increased danger and 60 days - for other work. The scope and content of the briefing is determined in each specific case, depending on the reasons and circumstances that necessitated its implementation.
Targeted instruction is carried out:
a) when performing one-time work not in the specialty (loading, unloading, etc.);
b) when carrying out work for which a permit or permit is issued;
c) during the liquidation of an accident or natural disaster;
d) during excursions and public events. The targeted briefing is formalized with a work permit or other documentation authorizing the work.
Primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings carried out by the work manager (foreman, head of a workshop, section, teacher, etc.). The verification is carried out by oral questioning or using technical means. An entry is made in the journal about the conduct of initial, repeated or unscheduled briefing, about permission to work, with the obligatory signatures of the person being instructed and the person instructing.
Magazines must be numbered, laced and sealed. The legislation of Ukraine provides for the forms of journals, the content of briefings, approximate lists of questions for introductory and initial briefing, approximate lists of introductory and initial briefing surveys, a plan and program for training officials and specialists on labor protection issues, a list of high-risk jobs.
Question 58. Types of briefings in the workplace, their purpose and frequency
Types of briefings
Instructions are important in ensuring occupational safety. According to GOST 12.0.004-90, five types of instruction are provided:
primary;
repeated;
unscheduled;
Induction training– carried out upon entry to work by the enterprise’s labor protection service. All new entrants to the enterprise, as well as business travelers and students arriving for internship are required to undergo this instruction. The purpose of this training is to introduce general rules and labor protection requirements at the enterprise.
Initial briefing– is carried out for all those hired at the enterprise before being allowed to work (including students arriving for internship), as well as upon transfer from one unit to another. Instruction is carried out directly at the workplace. The purpose of this briefing is to study the specific requirements and safety rules when working on specific equipment and when performing a specific technological process.
All workers, after initial instruction at the workplace, must, depending on the nature of the work and qualifications, undergo an internship for 2...14 shifts under the supervision of a person appointed by order (instruction) for the workshop (site, etc.). Workers are allowed to work independently after an internship, testing of knowledge and acquired skills in safe working methods.
Re-briefing - carried out at least once every six months, and for high-risk work - once a quarter. The purpose of this briefing is to restore labor safety rules in the employee’s memory, as well as to analyze existing violations of safety requirements in the practice of a production site, workshop, or enterprise.
Unscheduled briefing– carried out in the following cases:
upon the introduction of new or revised standards, rules, instructions on labor protection, as well as changes and additions to them;
when changing the technological process, replacing or upgrading equipment, devices and tools, raw materials, materials and other factors affecting safety;
during breaks in work for work that is subject to increased safety requirements, for more than 30 calendar days, and for others - 60 days;
at the request of supervisory authorities.
Targeted briefing– carried out when performing one-time work not related to direct duties in the specialty:
loading and unloading operations, one-time work outside the enterprise, workshop, site, etc.;
liquidation of accidents, catastrophes and natural disasters;
carrying out work for which a permit, permit or other special documents are issued;
conducting excursions to the enterprise, organizing public events with students (sports events, hikes, etc.).
Registration of briefings
Primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings are carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work (foreman, industrial training instructor, teacher). The person who conducted the instruction and internship makes an entry in the instruction logbook and (or) in the personal card of the instructee with the obligatory signature of the instructee and the instructor about the conduct of the specified briefings, internship, and admission to work. When registering an unscheduled briefing, indicate the reason for it. Targeted briefing with employees carrying out work under work permits, permits, etc. (provided for certain types of work of increased danger), is mandatory recorded in the work permit, permit or other document authorizing the work.
Check of knowledge
Knowledge testing is a necessary component of training and instruction. The results of the instruction are verified by oral questioning or using technical training tools, as well as by testing the acquired skills in safe working methods. Persons who demonstrate unsatisfactory knowledge are not allowed to work and are required to undergo training or instruction again.
Summary table of types of labor safety briefings









