How to properly use personal protective equipment. Personal protective equipment for skin
In protecting the population from weapons mass destruction along with sheltering the population in protective structures, evacuating and dispersing the population significant role belongs to the timely and correct use of personal and medical protective equipment for the population. The need to use these means of protection can be explained by the fact that the population and civil defense formations, when using nuclear, chemical or bacteriological weapons, will have to stay for a certain time or carry out rescue work in a terrain or atmosphere contaminated with radioactive substances, 0V or BS.
Facilities personal protection usually divided into:
a) respiratory protection equipment;
b) skin protection products;
c) medical supplies.
To organ protection means respiratory protection includes gas masks, respirators and simple means manufactured by the population themselves.
Gas masks. Modern gas masks have sufficiently high protective properties and performance indicators that provide protection to the human respiratory system and eyes from exposure to 0V (vapors, fog, gas, smoke, droplet liquid 0V), radioactive substances in the air, as well as from pathogenic microorganisms and toxins, in an aerosol state.
Gas masks are insulating and filtering. The most widely used are filter gas masks (combined arms, civilian, children); their device is based on the principle of purifying contaminated air in the inner layers of a filter-absorbing box in which carbon (catalyst) and an anti-aerosol (anti-smoke) filter are placed.
Protection of the human respiratory system from carbon monoxide, which is not retained by the protective layers of the filter-absorbing box, is ensured by using a special (hopcalite) cartridge, which is inserted (screwed) between the connecting tube (front part) of the gas mask and the filter-absorbing box.
Currently, in the country's civil defense system for the adult population, filtering gas masks GP-5, GP-5m and GP-7 can be used; for the protection of children - filtering gas masks DP-BM (children's gas mask, type six, small), DP-6 (children's gas mask, type six), PDF-7 (children's filtering gas mask, type seven), PDF-D (children's filtering gas mask, preschool) and PDF-Sh (children's filtering gas mask, school).
In addition, to protect children under 1 year of age, there is a KZD-6 (child protective camera, type six).
Non-standard gas masks include industrial gas masks, especially those used in chemical plants. The boxes of these gas masks are specialized; the charge may contain various absorbers or an absorber and an aerosol filter.
F
Fig.2. Filtering gas mask
The GP-5m gas mask kit includes a helmet - a mask with a membrane box (the box contains an intercom). The front part of gas masks GP-5 and GP-5n does not have a connecting tube and is directly connected to the filter-absorbing box. Helmet masks are available in five heights (with a membrane box - four). Their height is indicated by a number on the chin part of the helmet - the mask.
To select a gas mask of the GP-5 type, measure the head along a closed line passing through the crown, cheeks, and chin. The result obtained is rounded to 0.5 cm. For a measurement of up to 63 cm (for a helmet - a mask with a membrane box - up to 61 cm), zero height is taken, from 63.5 to 65 cm (from 61.5 to 64 cm) - 1 1st, from 65.5 to 68 cm (from 64.5 to 67 cm) - 2nd, from 68.5 to 70.5 cm (from 67.5 and more) - 3rd, from 71 cm and more - 4th height of the helmet - masks.
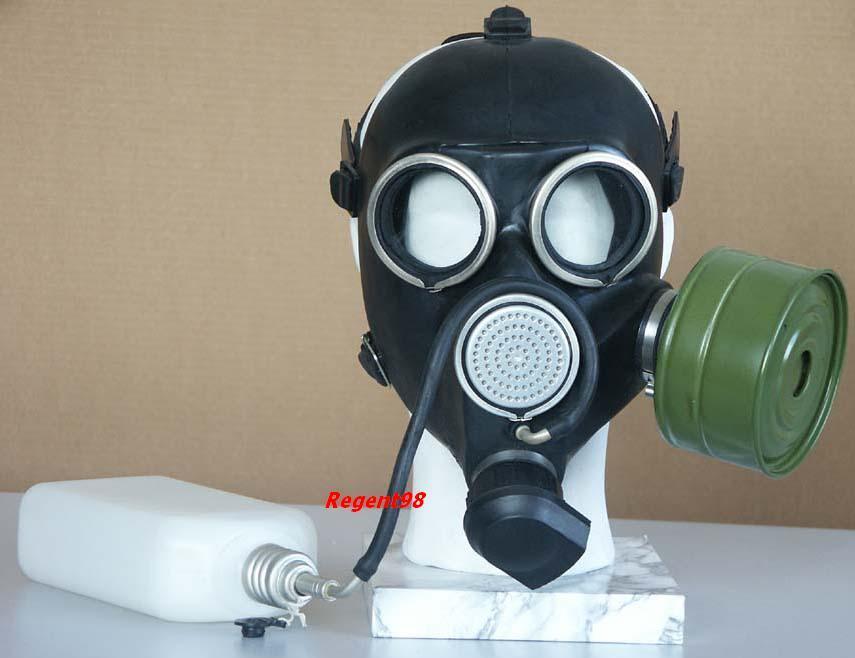

Fig.3. Filtering gas mask GP-7V
The GP-7 gas mask is produced in two modifications, differing in their front parts - GP-7 (Fig. 2) and GP-7V (Fig. 3). The GP-7 gas mask is equipped with an MGP front part with an intercom and without a drinking device.The GP-7V gas mask is equipped with an MGP-V front part with an intercom and a device for drinking from a standard army flask, which makes it possible to receive water in a contaminated atmosphere.
The selection of the front part of the gas mask GP-7 (GP-7V) is carried out based on the results of determining the horizontal and vertical girth of the head using a centimeter tape. Horizontal girth is determined by measuring the size of the head along a closed line running from the front along the brow ridge, from the side 2-3 cm above the edge of the auricle and from the back through the most protruding point of the head. Vertical girth is determined by measuring the size of the head along a closed line passing through the crown, cheeks and chin. The sum of both measurements determines the height of the mask. So, if the sum of the horizontal and vertical girths of the head is 118.5 - 121 cm, then this corresponds to the 1st height of the mask; 121.5 - 126.0 cm - 2nd height, 126.5 cm and more - 3rd height.
Children's gas masks have some design features in their design. Gas masks DP-6M are intended for young children (over one and a half years old). They are equipped with lightweight filter-absorbing boxes of type DP-6M and, as the front part, masks MD-1 (children's mask, type one) of four heights (1, 2, 3 and 4).
DP-6 gas masks are intended for older children; they are equipped with larger filter-absorbing boxes and, as a front part, MD-1 masks of one 5th height.
PDF-7 gas masks are intended for children of younger and older age; they are equipped with filtering and absorbing boxes of the GP-5 type (like a GP-5 gas mask for adults) and MD-1 masks of all five heights as the front part.
PDF-D gas masks are intended for children from 1.5 to 7 years old. They are equipped with filtering and absorbing boxes of type GP-5 and, as a front part, masks MD-3 (children's mask, type three) of four heights (1, 2, 3 and 4).
PDF-Sh gas masks are intended for children from 7 to 17 years old; They are equipped with filtering and absorbing boxes of the GP-5 type and, as the front part, with MD-3 masks of two heights (3rd and 4th) or helmets - masks of four heights (0.1, 2 and 3rd).
The design (with the exception of the features noted above) and the principles of operation of children's gas masks are similar to those of gas masks for adults.
Insulating gas masks (type IP-4, IP-46, Fig. 7) or oxygen isolating devices (KIP-5, KIP-7, KIP-8) completely isolate the human respiratory system from the outside air; breathing occurs due to oxygen released from the regenerative cartridge or supplied from the oxygen cylinder. These gas masks and devices are used for work if there are: high concentrations of 0B in the air, when a dangerous “slip” of 0B is possible and the filtering gas mask does not provide adequate protection; lack of oxygen content; high concentrations of carbon monoxide.
Based on the principle of providing oxygen, insulating gas masks and devices are divided into two groups: with chemically bound and with compressed oxygen. Gas masks of the first group include IP-4, IP-46, IP-46m; Gas masks of the second group include insulating devices KIP-5, KIP-7, KIP-8.
Respirators. To protect the respiratory system from aerosols (dust) RV, BS, toxic fumes, respirators are used: for adults - R-2, for children - R-2d. The R-2 respirator is a filtering half mask that allows for repeated use and staying in it for up to 12 hours.
The R-2d respirator is a modification for children; it is smaller in size and ensures continuous use for 4 hours.
The simplest means of respiratory protection. These products can be used by the public as respirators. They are simple in design and are therefore recommended as mass media protection made by the population itself. Such products include anti-dust fabric masks PTM-1 and cotton-gauze bandages. Every person should have them at their place of residence and work.
The PTM-1 mask consists of two main parts - the body and the mount. The body is made of 2 - 4 layers of fabric. It has inspection holes cut out with glass or transparent film inserted into them. The mask is attached to the head with a strip of fabric sewn to the side edges of the body. A tight fit of the mask to the head is ensured with the help of an elastic band in the top seam and ties in the bottom fastening seam, as well as a transverse elastic band sewn to the upper corners of the mask body. The air is purified by the entire surface of the mask as it passes through the fabric during inhalation.
Cotton gauze bandages are made from a piece of gauze measuring 100x50 cm. A layer of cotton wool measuring 30x20 cm and 2 cm thick is laid in the middle of a piece of gauze, the free edges of the gauze are folded over the cotton wool, and the ends are cut in the middle for ties. The lower ends are tied at the crown, and the upper ends at the back of the head. The cotton-gauze bandage should tightly cover the mouth and nose. It is suitable for one-time use. In the absence of the specified means, use towels, scarves, handkerchiefs, etc. Dust goggles can be used to protect the eyes from radiation.
Skin protection products are intended to protect open areas of skin, clothing, equipment and shoes from contact with droplets of liquid 0V, pathogens of infectious diseases, radioactive dust, and also partially from exposure to light radiation. They are divided into service (03K, L-1) and improvised (items of household clothing). According to the principle of action, standard means are divided into filtering (air-permeable) and insulating (air-tight).
Protective clothing made from filtering materials is intended for permanent or periodic wear. The basis of this clothing is cotton uniforms treated with a special chemical composition. Due to its sanitary and hygienic properties, it is suitable for everyday wear.
Filtering skin protection products include a set of filter clothing ZFO-58; it consists of a cotton overall of a special cut, impregnated with a solution of a special paste - chemical substances that retain OM vapors (adsorption type) or neutralize them (chemo-sorption type), as well as men's underwear (shirt and underpants), a cotton balaclava and two pairs of foot wraps (one of which is impregnated with the same composition as the overalls). Underwear, a balaclava and an unimpregnated pair of foot wraps are used to prevent the overalls from abrading the skin and irritating it from the impregnating composition. The sizes of the overalls included in the ZFD set: the first - for people up to 160 cm tall, the second - from 160 to 170 cm and the third - over 170 cm.
Insulating skin protection products made from airtight materials can be hermetically sealed (suits, overalls that cover the entire human body and protect against drops and 0V vapors) and partially or completely non-thermetic (raincoats, capes, aprons, etc.), which mainly protect from droplet liquid 0V: OZK set, light protective suit (L-1), protective overalls or suit.
The OZK set (Fig. 4, 5), which includes a raincoat, protective stockings and gloves, is usually used with impregnated uniforms (clothing) and underwear.


Fig.4. OZK in the form of overalls, gas respirator, chemical safety goggles.
Fig.5. OZK in the form of a raincoat, PMG.
The light protective suit L-1 (Fig. 6) is made of rubberized fabric and consists of a shirt with a hood, trousers sewn together with stockings, two-fingered gloves and a balaclava.
Insulating skin protection products are intended for personnel civil defense formations. They are used when working in contaminated areas under conditions of high concentrations of 0V, as well as when performing degassing, decontamination and disinfection work.
To protect against radioactive dust, the population can also wear ordinary clothing. To ensure its tightness, you need to have additional devices; bibs, hood, side trouser fasteners. To protect against radiation, you can also use available skin protection products (personal, household, sports, industrial and other clothing and shoes with additional sealing agents).

Fig.7. Isolating suit KIKH-4,
insulating gas mask IP-4
Fig.6. L – 1, PMG
It should be remembered that being in insulating protective clothing is far from indifferent to a person, since especially in the hot season, heat transfer and heat transfer are disrupted, which in turn leads to sudden overheating of the body. As a result, breathing and cardiac dysfunction are observed; in severe cases, heat stroke may occur. For this reason, the work and stay of people in insulating protective clothing is limited in time.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is designed to preserve the combat effectiveness of personnel of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation and ensure the fulfillment of a combat mission in conditions of the enemy’s use of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), as well as in conditions of exposure to damaging environments that arise during the operation and damage of weapons and equipment. military equipment.
Timely and skillful use of PPE provides reliable protection from toxic substances (0B), light radiation from nuclear explosions (LNE), radioactive dust (RP), radioactive substances (RS), bacterial (biological) aerosols (BA), carbon monoxide and allows you to perform certain tasks underwater and in oxygen-deprived environments. PPE also provides short-term protection from fire mixtures and open flames.
In order to increase the protection of personnel, along with PPE, medical supplies included in the individual first aid kit, as well as an individual anti-chemical package, are used.
Personal protective equipment is divided into personal respiratory protection equipment (RPPE), personal eye protection equipment (PEPE) and personal skin protection equipment (PEPE).
Based on the principle of protective action, RPE and SIZK are divided into filtering and insulating.
According to their purpose, PPE is divided into general and special. General-arms PPE is intended for use by personnel of all or several branches of the Armed Forces of the USSR and branches of the military. Special PPE is intended for use by military personnel of certain specialties or for performing special work.
RPE includes gas masks, respirators, self-contained breathing apparatus (IBA), kit additional cartridge(KDP), hopcalite cartridge.
SIDH includes protective glasses from SIYAV.
PPE includes protective clothing of the filtering and insulating type, made of filtering and insulating materials, respectively.
Depending on the principle of combat use and the frequency of use, personal protective equipment is divided into means of constant and periodic wear, means of single and multiple use. Personal protective equipment is used in the “traveling”, “ready” and “combat” positions.
In the “stowed” position, PPE is part of wearable or transportable equipment, ready for its intended use. When operating in closed mobile objects of weapons and military equipment and in fortifications or at a distance closest to them, PPE in the “stowed” position can be placed in places specified by the unit commander.
In the “ready” position, PPE is used to reduce the time it takes to transfer it to the “combat” position in conditions of sudden use by the enemy of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons based on the first signs (reliable or unreliable).
The first signs of the enemy's use of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons are: a massive artillery attack; characteristic dull explosions of ammunition; air or missile strikes and overflights of aircraft, including small groups, at low altitudes; the appearance of smoke and fog of unknown origin; specific foreign odors; watering from aircraft pouring devices; indications of technical means of chemical and nonspecific bacteriological (biological) reconnaissance; change in color of the indicator film.
PPE is transferred to the “combat” position immediately in conditions of sudden use by the enemy of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons or in advance.
In the “combat” position, PPE “gases” are used to protect against 0V and BA. In the “gases” position, PPE also provides protection from nuclear explosives, RP and short-term protection from fire mixtures and open flames.
In the “combat” position, “atom” PPE is used to protect against nuclear weapons and RP. In the “atom” position, PPE also provides short-term protection from fire mixtures and open flames.
To transfer all personal protective equipment available to personnel to the “ready” position, the command “Prepare protective equipment” is given.
PPE is transferred to the “combat” position “gases” by the “Chemical alarm” signal, by the command “Gases, raincoats” for immediate donning in conditions of sudden use of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons by the enemy and the command “Put on protective equipment in the “gases” position "(in conditions of putting on PPE in advance).
The protective raincoat in the form of overalls, together with a gas mask and other personal protective equipment, is transferred to the “combat” position by the command “Put on the protective suit. Gases"; special protective clothing - “Wear protective clothing. Gases."
PPE is transferred to the “combat” position “atom” by the signal “Radiation hazard” or by the command “Put on protective equipment in the “atom” position.”
To transfer only the gas mask and only the respirator to the “combat” position, the commands “Gases” and “Put on the respirator” are given, respectively.
To clarify the list of PPE prepared for use and used and its position, in addition to the main command (or without it), a clarifying command or instructions are given, for example: “Put on protective equipment in the “gas” position”, “OZK - in the stowed position”, etc. . P. Removal of PPE is carried out only with the permission of the commander.
To remove PPE, the command “Remove protective equipment” is given. If it is necessary to remove only individual PPE, a clarifying command is given, for example: “Remove the protective raincoat.” In the event of infection of personnel with BA, removal of the gas mask and PPE is allowed only after complete special treatment of weapons and military equipment. The gas mask is removed during complete sanitization of personnel.
The list of PPE and the procedure for its use, including the determination of the boundaries and time of transfer of PPE to the “combat” position and its removal, is determined by the unit commander, based on the conditions of the combat mission, the likelihood of exposure of personnel to certain damaging factors of weapons of mass destruction in specific conditions, taking into account climatic (weather) factors, as well as the protective, operational and ergonomic characteristics of PPE. In this regard, recommendations should be applied in accordance with the specific situation.
Skillful use of PPE is achieved by constant training of personnel. At the same time, special attention when training personnel in the use of PPE should be paid to: acquisition by personnel of knowledge about the purpose, design and procedure for transferring PPE to a “combat” position in various conditions; acquiring stable skills of holding your breath when performing work with various physical loads; the ability to correctly and quickly put on a gas mask and a cloak-like cloak; skills acquisition correct translation in the “combat” position of PPE; developing the ability to effectively operate weapons and military equipment while wearing PPE, especially when worn for a long time; training in the correct use of PPIs and degassing agents; mastering the skills and rules of first aid, self- and mutual assistance in case of exposure to 0V, asthma and ionizing radiation.
Maintaining PPE in good condition and constant readiness for use is achieved by observing the rules for their conservation, timely and high-quality repairs and maintenance in accordance with the requirements of the “Charter of Internal Service of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation” and the recommendations of the “Manual for the operation of personal protective equipment.”
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
in the discipline: “LIFE SAFETY”
topic: “PROCEDURE FOR APPLICATION OF PERSONAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT”
Lipetsk 2011
I. COMPOSITION AND PURPOSE OF PERSONAL PROTECTION EQUIPMENT
Personal protective equipment is designed to protect people from the ingress of radioactive and toxic substances and bacterial agents into the body, skin and clothing.
Personal protective equipment is divided into respiratory protection and skin protection.
Respiratory protection equipment includes:
b Gas masks (filtering and insulating);
b Respirators;
b Anti-dust fabric masks PTM-1;
b Cotton-gauze bandages.
Skin protection products include:
b Protective kits;
b Overalls and suits made from special rubberized fabric;
ь Capes;
b Rubber boots and gloves;
ь Various available means.
According to the principle of protection, personal protective equipment is divided into:
1. Filtering;
2. Insulating.
According to the manufacturing method, personal protective equipment is divided into:
1) Manufactured by industry;
2) Protozoa, made by the population from scrap materials.
II. RESPIRATORY PROTECTION, THEIR PURPOSE AND RULES OF USE
The most reliable means of protecting people's respiratory organs is a gas mask. It is designed to protect the respiratory system, face, eyes, and sometimes the scalp from harmful impurities in the air in the form of steam, fog, gas, smoke, droplets, microbes and their toxins.
All gas masks are divided into filtering and insulating based on their operating principle. A person wearing a filter gas mask breathes pre-purified air, and a person wearing an insulating gas mask breathes a mixture of oxygen in the cylinder and exhaled air after it has been cleared of moisture and carbon dioxide.
Filtering gas masks.
The main filter gas masks include civilian gas masks GP-5 (GP-5M and GP-7 (GR-7V)).
The civilian gas mask GP-5 is designed to protect a person from contact with the respiratory system, eyes and face of radioactive, toxic and emergency chemically hazardous substances, and bacterial agents.
To select the required helmet-mask size (0, 1, 2, 3, 4), you need to measure your head along a closed line passing through the crown, cheeks and chin; measurements are rounded to the nearest 0.5 cm.
The GP-5M gas mask differs from the GP-5 in the presence of a ShM-66U helmet-mask with a membrane box for the intercom, in the front part of which there are through cutouts for the ears, which ensures normal audibility.
The gas mask is carried in the bag. The shoulder strap is thrown over the right shoulder, and the bag itself is lowered to the left side, with the flap facing away from you.
The gas mask can be in the following positions: “travelling”, “ready”, “combat”. The gas mask is in the “stowed” position when there is no threat of infection. The top of the bag should be at waist level and the flap should be fastened. The gas mask is switched to the “ready” position when there is a threat of infection, after information on the radio or upon the command “Get your gas masks ready!” In this case, the bag is secured with a belt strap, moved slightly forward, and the valve is unfastened so that you can quickly use the gas mask. In the “combat” position, the front part is put on. This is done with the command “gases!” or by other orders, as well as independently if signs of a particular infection are detected.
When transferring the gas mask to the combat position, you must:
Hold your breath and close your eyes;
Remove the headdress and hold it between your knees or place it next to it;
Take the helmet-mask out of the bag, grab it with both hands by the thick edges at the bottom so that thumbs the hands were on the outside, and the rest on the inside. Bring the helmet-mask to your chin and with a sharp movement of your hands up and back, pull it over your head so that there are no folds at the top;
Exhale completely, open your eyes and resume breathing;
Put on a hat, fasten the bag and secure it to the body, if this has not been done previously.
The gas mask is considered to be worn correctly if the glasses of the front part are against the eyes and the helmet-mask fits tightly to the face. The need to exhale forcefully before opening your eyes is explained by the fact that it is necessary to remove contaminated air from under the mask if it got there at the time of putting it on.
When wearing a gas mask, you should breathe deeply and evenly. There is no need to make sudden movements. If you need to run, then increase the pace gradually.
The gas mask is removed by the command “take off the gas mask!” To do this, you need to lift the headgear, take the valve box with the other hand, slightly pull the helmet-mask down and remove it with a forward and upward movement, put on the headgear, turn out the helmet-mask, wipe it thoroughly and put it in the bag.
In winter, to prevent the rubber from hardening, you should periodically heat the front part of the gas mask by placing coats, jackets, etc. under the side. When wearing a gas mask, you can heat the valves with your hands while simultaneously blowing them out with a sharp exhalation.
The civilian gas mask GP-7 is one of the latest models. It reliably protects against many toxic and chemically hazardous substances, radioactive dust and bacterial agents. Compared to the GP-5, it has a number of advantages: breathing resistance is reduced, an “independent” seal (shutter) provides a more reliable seal and at the same time reduces the pressure of the front part on the head. This made it possible to increase the time spent in a gas mask and to use it for people over 60 years of age, patients with pulmonary and cardiovascular diseases. The presence of an intercom ensures clear understanding of speech.
The front part of the gas mask is made in three sizes. The selection of what is necessary is carried out based on the results of measuring the horizontal and vertical circumference of the head with a soft centimeter tape. Vertical girth - measurement along a closed line passing through the crown, cheeks and chin. Horizontal girth - measuring the head along a closed line passing from the front along the brow ridges, from the side - 2-3 cm above the edge of the auricle and from the back - through the most protruding point of the head. Measurements are rounded to the nearest 0.5 cm.
When putting on a gas mask, it is necessary to remove hair from the forehead and temples. If they get under the seal, the seal will break. Therefore, women should comb their hair smoothly back, remove hairpins, combs, pins and jewelry.
To properly put on the GP-7, you need to take its front part with both hands by the cheek straps so that your thumbs grip them from the inside. Then fix the chin in the lower recess of the seal and move your hands up and back to pull the headband over your head, pulling the cheek straps all the way.
The GP-7V gas mask differs from the GP-7 in that it has a device for receiving water.
Additional cartridges. Tests have shown that civilian gas masks GP-5 and GP-7, as well as children's gas masks PDF-7, PDF-D, PDF-1, PDF-2D, PDF-2, along with protection from hazardous agents, protect against some hazardous chemicals, for example such , such as chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, hydrochloric acid, hydrocyanic acid, tetraethyl lead, nitrobenzene, phenol, phosgene, cyanogen chloride, etc.
In order to expand the capabilities of gas masks to protect against hazardous chemicals, additional hopcalite cartridges have been created for them (DPG-1 and DPG-3). Inside the DPG-1 cartridge there are two layers - a special absorber and hopcalite. In DPG-3 there is one layer of absorber. The outside air, entering the filter-absorbing box of the gas mask, is pre-cleaned of aerosols and vapors of hazardous substances, then entering the additional cartridge, it is finally cleared of harmful impurities.
The cartridge has a cylindrical shape and is similar in appearance to the filter-absorbing box of gas masks GP-5, GP-7. At the bottom there is an internal thread cut for connection to the GP-5 or GP-7 filter-absorbing box.
Respirators.
They are lightweight means of protecting the respiratory system from harmful gases, vapors, aerosols and dust. They are widely used in mines, mines, chemically harmful and dusty enterprises, and when working with fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture. They are used at nuclear power plants, when cleaning scale at metallurgical enterprises, during painting, loading and unloading and other work.
There are two types of respirators:
® Respirators in which the half mask and filter element simultaneously serve as the front part;
® Respirators that purify the inhaled air in filter cartridges attached to a half mask.
According to their intended purpose, respirators are divided into:
® Anti-dust;
® Gas protection;
® Gas-dust-proof.
Dust respirators protect the respiratory system from aerosols various types, gas protection - from harmful vapors and gases, gas and dust protection - from gases, vapors and aerosols with their simultaneous presence in the air.
Depending on the service life, respirators are disposable (ShB-1 “petal”, “Kama”, U-2K, R-2), reusable(RPG-67, RU-67M). secondly, replacement of filters is provided.
The simplest means of respiratory protection.
When there is neither a gas mask nor a respirator, you can use the simplest means of protection - an anti-dust fabric mask (PTM), a cotton-gauze bandage. They reliably protect the human respiratory system (and PTM - the skin of the face and eyes) from radioactive dust, harmful aerosols, and bacterial agents.
The PTM-1 mask consists of two main parts - the body and the mount. The housing has inspection holes into which glass or plates of plexiglass, celluloid or some other transparent material are inserted.
The body of the mask is made of 4-5 layers of fabric. The top layer is made of loose fabric - calico, staple, cotton or knitted fabric, tartan, etc. The inner layers (there can be 2-3 of them) are made of denser fabrics - paper, flannel, flannel, children's pique, cloth, cotton or wool brushed fabrics. The bottom layer can be made of satin, knit and other non-fading fabrics.
The fastening of the mask is made from one layer of any fabric, preferably lining or linen.
A cotton-gauze bandage is made as follows:
® Take a piece of gauze 100*50cm;
® In the middle part of the piece, on an area of 30*20 cm, place an even layer of cotton wool approximately 2 cm thick;
® The cotton-free ends of the gauze (about 30-35 cm) on both sides are cut in the middle with scissors, forming two pairs of ties;
® The ties are secured with thread stitches (sewn).
If you have gauze, but no cotton wool, you can make a gauze bandage. To do this, instead of cotton wool, 5-6 layers of gauze are placed in the middle of the piece.
When used, a cotton-gauze (gauze) bandage is applied to the face so that its lower edge covers the bottom of the chin, and the upper edge reaches the eye sockets, while the mouth and nose should be well covered. The cut ends of the bandage are tied: the lower ones - on the crown, the upper ones - on the back of the head. To protect the eyes, dust glasses of various types are used. You can make glasses yourself.
In order to make protection against hazardous chemicals more reliable, for example, if a cloud of chlorine is approaching, it is recommended to moisten the bandage with a 2% solution of baking soda, and to protect against ammonia - with a 5% solution of citric (acetic) acid.
It is not recommended to use cotton-gauze bandages for a long time.
A cotton-gauze bandage and an anti-dust fabric mask do not protect against many hazardous substances.
III. SKIN PROTECTION PRODUCTS, THEIR PURPOSE AND RULES OF USE
In conditions of radiation, chemical and bacteriological contamination, in accidents associated with the storage and transportation of hazardous chemicals, natural disasters, sabotage, contributing to the contamination of vast territories with high concentrations of harmful substances and long time, there is an urgent need to protect the human body.
According to their purpose, skin protection products are divided into:
® Special (service);
® Helpers.
Special (service) means.
Special skin protective equipment is intended to protect personnel of formations when they carry out rescue and emergency restoration work in areas of nuclear, chemical and bacteriological damage (destructions, accidents and disasters).
According to the principle of protective action, they are:
® Insulating (airtight);
® Filtering (air-permeable).
Structurally, these protective equipment are usually made in the form of jackets with hoods, bib overalls and overalls.
To protect against chemical agents and hazardous chemicals in the zone of chemical contamination, insulating type protective equipment is mainly used.
Insulating protective equipment.
Insulating clothing is made from materials that do not allow any drops or vapors of toxic substances to pass through, thereby ensuring the necessary tightness.
Isolating protective equipment includes: light protective suit L-1, protective overalls and suit, general protective kit.
Light protective suit L-1 provides skin protection from exposure agents, radiation exposure and BS during various works. The suit is made in three sizes (the first is for people up to 165 cm tall; the second is from 165 to 172 cm; the third is above 172 cm).
The protective overalls consist of trousers, a jacket and a hood sewn into one piece. It is made from rubberized fabric. Used to protect the skin when performing work in highly contaminated conditions.
The protective suit includes a jacket, trousers, rubber gloves, boots and a balaclava.
The combined arms protective kit consists of a protective raincoat, rubber boots and protective gloves. To protect against vapors, special uniforms are worn underneath the kit.
The protective raincoat comes in five sizes (the first - for people up to 165 cm tall; the second - from 165 to 170 cm; the third - from 170 to 175 cm; the fourth - from 175 to 180 cm; the fifth - above 180 cm). The cloak can be worn as a jumpsuit, a cape, or worn in sleeves.
Filter protection means.
Filter protection means are made from cotton fabric impregnated with special chemicals. As a result, the air permeability of the material is largely preserved, and vapors of toxic and toxic substances passing through the fabric are retained by the impregnation. In some cases, neutralization occurs, and in others, sorption (absorption).
Filtering agents include a set of protective filter clothing in the Western Federal District. The main purpose of this kit is to protect human skin from the action of chemical agent vapors. The kit also provides protection against aerosol agents.
The simplest skin protection products.
The simplest means of protecting the skin can be used, first of all, industrial clothing: jackets, trousers, overalls, robes with hoods, mostly made from tarpaulin, fire-retardant or rubberized fabric, coarse cloth. They are capable of protecting not only radioactive substances from contact with the skin during accidents at nuclear power plants and other radiation hazardous facilities, but also from droplets, vapors and aerosols of many hazardous chemicals. Tarpaulin products, for example, protect against droplet-liquid hazardous substances for up to 1 hour in winter, and up to 30 minutes in summer.
Among items of household clothing, the most suitable for this purpose are raincoats and capes made of rubberized fabric or fabric covered with vinyl chloride film complete with a cotton-gauze bandage or PTM-1.
Winter items can also provide protection: coats made of rough cloth or drape, padded jackets, sheepskin coats, leather coats. these items can protect for up to two hours, depending on specific weather and other conditions, the concentration and state of aggregation of hazardous chemicals.
Other types may also provide protection after appropriate treatment. outerwear: tracksuits, jackets, especially leather ones, denim clothes, raincoats made of waterproof fabric.
To protect your feet, it is best to use industrial or household rubber boots, rubber boots and galoshes. You can also use shoes made of leather and leatherette, but it is advisable to wear rubber galoshes over them. Rubber products are capable of preventing the passage of droplet-liquid hazardous substances for up to 3 - 6 hours.
You should put on rubber or leather gloves on your hands, you can use tarpaulin mittens, tie a scarf on your head or put on a hat with earflaps.
In order for ordinary clothing to better protect against vapors and aerosols of hazardous chemicals, it must be soaked in a special solution. Only clothing made from fabric materials can be impregnated. To impregnate one set of clothing and accessories (valve, hood, gloves, socks, etc.), 2.5 liters of solution is enough.
The impregnating solution can be prepared on the basis of aqueous synthetic detergents used when washing clothes. Another option uses mineral and vegetable oils.
poisonous radiation contamination bacteriological
IV. MEDICAL PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
The individual first aid kit AI-2 is designed to prevent the development of shock, radiation sickness, damage caused by organophosphorus substances, as well as infectious diseases. Comes in a plastic flat pack orange color(more often).
AI-2 includes seven therapeutic and prophylactic drugs (drugs):
® Analgesic agent in a syringe tube;
® a remedy used for organophosphorus poisoning;
® radioprotective agent №1;
® radioprotective agent No. 2;
® antibacterial agent No. 1;
® antibacterial agent No. 2;
® antiemetic.
The individual anti-chemical package IPP-8 is intended for decontamination of skin and clothing when affected by organophosphorus compounds, toxic substances of blister action (mustard gas), for disinfection, and washing off radioactive substances from the skin.
IPP-8 includes:
® Glass bottle containing degassing liquid;
® Hermetically sealed plastic bag, containing five gauze pads and instructions.
Posted on Allbest.ru
Similar documents
History of the development of personal respiratory protection equipment. The role and place of personal protective equipment in common system protection in peacetime and wartime emergencies. Purpose and classification of skin protection products. Medical personal protective equipment.
course work, added 06/03/2014
Consideration of the main types of respiratory protection equipment. Classification, design and principles of operation of gas masks, respirators, simple personal protective equipment. Studying ways to protect the skin from exposure to chemicals.
presentation, added 08/11/2014
Review and study of personal protective equipment as devices designed to protect the skin and respiratory system from exposure to toxic substances. Classification and quality control of personal protective equipment. Filtering, respiratory, insulating gas masks.
presentation, added 04/16/2011
Classification of personal protective equipment, organization and procedure for providing them. Characteristics and types of filtering and insulating gas masks. Means for protecting skin and exposed areas of the body. Medical supplies and personal protective equipment.
abstract, added 02/14/2011
Classification of personal protective equipment by protected areas. Respiratory protection: filtering and isolating respiratory protection. Specifics of the use of skin protection products, equipment and purpose medical supplies protection.
test, added 03/24/2010
Purpose of using personal protective equipment. Self-rescuer filter, with compressed air. Hose and self-contained breathing apparatus. Comparative characteristics personal respiratory protection equipment, self-rescuers and their cost.
practice report, added 04/26/2012
Classification of personal protective equipment. Organization and procedure for providing personal protective equipment. Methods of respiratory protection using gas masks and respirators. Features of the use of insulating and filtering skin protection products.
abstract, added 05/23/2015
Basic information about human safety in a production environment. Classification of personal protective equipment and features of their use in some industries. Quality control of personal protective equipment.
abstract, added 12/19/2010
Characteristics of filtering and isolating personal protective equipment for the population. Use of civil and industrial gas masks, dust respirators. Study of the classification and features of the use of personal skin protection products.
abstract, added 02/02/2016
The main ways to protect the population from chemical toxic substances are the use of personal respiratory protection equipment and specially equipped shelters. The procedure for notifying about a chemical threat and evacuating the population from areas of possible contamination.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is designed to preserve the combat effectiveness of personnel of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation and ensure the accomplishment of a combat mission in conditions of the enemy’s use of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), as well as in conditions of exposure to damaging environments that arise during the operation and damage of weapons and military equipment.
Timely and skillful use of PPE provides reliable protection from toxic substances (0B), light radiation from nuclear explosions (LNE), radioactive dust (RP), radioactive substances (RS), bacterial (biological) aerosols (BA), carbon monoxide and allows you to perform certain tasks underwater and in oxygen-deprived environments. PPE also provides short-term protection from fire mixtures and open flames.
In order to increase the protection of personnel, along with PPE, medical supplies included in the individual first aid kit, as well as an individual anti-chemical package, are used.
Personal protective equipment is divided into personal respiratory protection equipment (RPPE), personal eye protection equipment (PEPE) and personal skin protection equipment (PEPE).
Based on the principle of protective action, RPE and SIZK are divided into filtering and insulating.
According to their purpose, PPE is divided into general and special. General-arms PPE is intended for use by personnel of all or several branches of the Armed Forces of the USSR and branches of the military. Special PPE is intended for use by military personnel of certain specialties or for performing special work.
RPE includes gas masks, respirators, self-contained breathing apparatus (IBA), an additional cartridge kit (KDP), and a hopcalite cartridge.
SIZG includes protective glasses against SIYV.
PPE includes protective clothing of the filtering and insulating type, made of filtering and insulating materials, respectively.
Depending on the principle of combat use and the frequency of use, personal protective equipment is divided into means of constant and periodic wear, means of single and multiple use. Personal protective equipment is used in the “traveling”, “ready” and “combat” positions.
In the “stowed” position, PPE is part of wearable or transportable equipment, ready for its intended use. When operating in closed mobile objects of weapons and military equipment and in fortifications or at a distance closest to them, PPE in the “stowed” position can be placed in places specified by the unit commander.
In the “ready” position, PPE is used to reduce the time it takes to transfer it to the “combat” position in conditions of sudden use by the enemy of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons based on the first signs (reliable or unreliable).
The first signs of the enemy's use of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons are: a massive artillery attack; characteristic dull explosions of ammunition; air or missile strikes and overflights of aircraft, including small groups, at low altitudes; the appearance of smoke and fog of unknown origin; specific foreign odors; watering from aircraft pouring devices; indications of technical means of chemical and nonspecific bacteriological (biological) reconnaissance; change in color of the indicator film.
PPE is transferred to the “combat” position immediately in conditions of sudden use by the enemy of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons or in advance.
In the “combat” position, PPE “gases” are used to protect against 0V and BA. In the “gases” position, PPE also provides protection from nuclear explosives, RP and short-term protection from fire mixtures and open flames.
In the “combat” position, “atom” PPE is used to protect against nuclear weapons and RP. In the “atom” position, PPE also provides short-term protection from fire mixtures and open flames.
To transfer all personal protective equipment available to personnel to the “ready” position, the command “Prepare protective equipment” is given.
PPE is transferred to the “combat” position “gases” by the “Chemical alarm” signal, by the command “Gases, raincoats” for immediate donning in conditions of sudden use of chemical or bacteriological (biological) weapons by the enemy and the command “Put on protective equipment in the “gases” position "(in conditions of putting on PPE in advance).
The protective raincoat in the form of overalls, together with a gas mask and other personal protective equipment, is transferred to the “combat” position by the command “Put on the protective suit. Gases"; special protective clothing - “Wear protective clothing. Gases."
PPE is transferred to the “combat” position “atom” by the signal “Radiation hazard” or by the command “Put on protective equipment in the “atom” position.”
To transfer only the gas mask and only the respirator to the “combat” position, the commands “Gases” and “Put on the respirator” are given, respectively.
To clarify the list of PPE prepared for use and used and its position, in addition to the main command (or without it), a clarifying command or instructions are given, for example: “Put on protective equipment in the “gas” position”, “OZK - in the stowed position”, etc. . P. Removal of PPE is carried out only with the permission of the commander.
To remove PPE, the command “Remove protective equipment” is given. If it is necessary to remove only individual PPE, a clarifying command is given, for example: “Remove the protective raincoat.” In the event of infection of personnel with BA, removal of the gas mask and PPE is allowed only after complete special treatment of weapons and military equipment. The gas mask is removed during complete sanitization of personnel.
The list of PPE and the procedure for its use, including the determination of the boundaries and time of transfer of PPE to the “combat” position and its removal, is determined by the unit commander, based on the conditions of the combat mission, the likelihood of exposure of personnel to certain damaging factors of weapons of mass destruction in specific conditions, taking into account climatic (weather) factors, as well as the protective, operational and ergonomic characteristics of PPE. In this regard, recommendations should be applied in accordance with the specific situation.
Skillful use of PPE is achieved by constant training of personnel. At the same time, special attention when training personnel in the use of PPE should be paid to: acquisition by personnel of knowledge about the purpose, design and procedure for transferring PPE to a “combat” position in various conditions; acquiring stable skills of holding your breath when performing work with various physical loads; the ability to correctly and quickly put on a gas mask and a cloak-like cloak; acquiring the skills to correctly transfer PPE to the “combat” position; developing the ability to effectively operate weapons and military equipment while wearing PPE, especially when worn for a long time; training in the correct use of PPIs and degassing agents; mastering the skills and rules of first aid, self- and mutual assistance in case of exposure to 0V, asthma and ionizing radiation.
Maintaining PPE in good condition and constant readiness for use is achieved by observing the rules for their conservation, timely and high-quality repairs and maintenance in accordance with the requirements of the “Charter of Internal Service of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation” and the recommendations of the “Manual for the operation of personal protective equipment.”
Use of personal protective equipment
In the complex of measures to protect the population in man-made emergencies or when exposed to weapons of mass destruction of a possible enemy, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) occupies one of the leading places. PPE is necessary to protect the respiratory system when people are in an atmosphere of contaminated air with poisonous, radioactive hazardous chemical substances, biological agents, as well as to protect open areas of skin and clothing (uniforms) from contact with drops and aerosols of toxic and hazardous chemical substances, radioactive dust and biological agents. In addition, personal protective equipment is also used to protect the human body from the effects of heat flows and smoke aerosols in fire conditions, and from production factors that negatively affect human health. The use of PPE under conditions of exposure to thermal radiation and production factors is not discussed in this section.
According to their purpose, PPE is divided into personal respiratory protection equipment (RPP) and skin protection equipment (SPS), and according to the principle of protective action - into personal protective equipment of filtering and insulating types.
Personal respiratory protection includes industrially produced gas masks and respirators and simple protective equipment manufactured by the population, such as dust-proof fabric masks and cotton-gauze bandages.
Skin protection products include special protective clothing, made from rubberized and other insulating fabrics, as well as household clothing made from polyethylene and other moisture- and dust-proof materials.
Filtering personal protective equipment provides protection for the respiratory system and skin either by absorbing harmful impurities contained in the ambient air with special chemical absorbers, or by depositing large aerosols and solid harmful impurities in the atmosphere on fine-porous fabric materials.
Insulating protective equipment provides respiratory protection by supplying the human body with clean air obtained using autonomous systems without using outside air for these purposes. Skin protection is ensured in this case by its complete isolation from environment.
Personal respiratory protection
Filtering gas masks. Designed to protect against chemically hazardous substances, bacterial (biological) agents, radioactive vapors and aerosols entering the respiratory system, eyes and face of a person.
Filtering gas masks are produced by industry for workers and employees of chemically hazardous industries (industrial gas masks) and for the population (civilian gas masks). The intended purpose of industrial gas masks is protection production staff from hazardous chemicals when their concentrations in the air exceed permissible standards.
Depending on the type of hazardous chemicals used in the production, industrial gas masks are produced with various filter boxes (Table 4.4.1), each of which has a selective ability to absorb toxic substances in the ambient air. Their protective properties based on control concentrations of some hazardous chemicals are given in Table. 4.4.2.
Table 4.4.1
Nomenclature and purpose of industrial gas mask boxes
Note: Anti-gas boxes of brands with the index "8" have a resistance at a volumetric air flow rate of 30 l/min up to 80 Pa, without the index "8" - 180 Pa, with the index "f" - are equipped with anti-aerosol filters and are additionally marked on the box - "white stripe" ".
In accordance with current safety instructions, only production personnel of chemically hazardous industries (workshops, production areas, laboratories, etc.) are provided with industrial gas masks. Unfortunately, in a number of enterprises classified even as a first-degree chemical hazard, not all workers and employees are provided with security. Considering that in case of major chemical accidents all workers and employees of chemical dangerous object, in order to ensure its safety, it is necessary to provide all personnel with industrial gas masks.
As part of the declaration of chemically hazardous industries and facilities, today there is a need to provide industrial gas masks not only to all industrial and production personnel of chemically hazardous facilities, but also to production personnel of nearby facilities.
Table 4.4.2
Protective properties of large-sized industrial gas masks boxes for hazardous chemicals 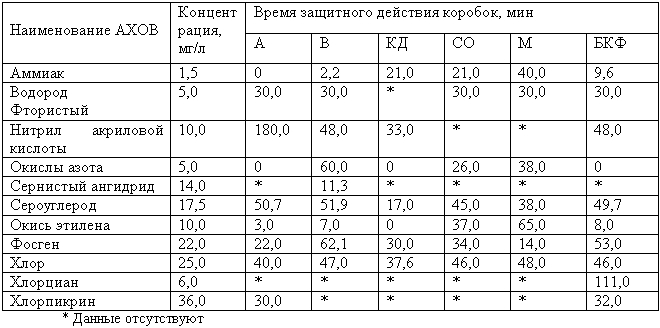
The data given in table. 4.4.2 show that industrial filter gas masks have a sufficiently high sorption capacity, which allows them to be used at concentrations of hazardous substances many times higher than permissible. However, it must be taken into account that in conditions of industrial or other accidents associated with the release of hazardous chemicals into the atmosphere, in close proximity to the source of danger, the concentrations of toxic substances may be so high that the use of these gas masks may be unsafe. In such situations, industrial gas masks can only be used to exit (evacuate) personnel to the safe territory of the facility.
Gas-dust respirators. At relatively low concentrations (10-15 MAC), gas-dust respirators can be used to protect the respiratory system from vapors, gases, and aerosols of hazardous chemicals: RU-60M with KD and V cartridges, RPG-67 with KD cartridge and “Snezhok-GP-E”.
Respirators RU-60M and RPG-67 are manufactured in the form of a PR-7 rubber half mask with a knitted seal. RU-6OM is used with two absorbing cartridges, which house the charge and the filter. RPG-67 is used with a KD cartridge without a filter and protects only from vapors and gases of hazardous chemicals. The gas-dust respirator "Snezhok-GP-E" has dust-aerosol and absorption filters that provide protection both from aerosols and vapors, and from hazardous gases (hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen chloride, chlorine and sulfur dioxide).
In all cases, gas-dust respirators have limited use. They cannot be used if hazardous substances affect the eyes and skin. They are used in industry in accordance with the rules of industrial sanitation to protect the respiratory system not only from harmful substances, but also from mechanical impurities suspended in the air of the production room.
Civilian gas masks. More accessible to the population are civilian gas masks, of which the country has accumulated in such quantities that it is quite sufficient to provide the entire population living in areas at risk of emergencies as a result of large-scale releases of hazardous chemicals into the environment.
It's about about gas masks that were accumulated and stored in special warehouses to ensure the protection of the population in war time. Their main purpose is to protect the respiratory system from toxic substances of a potential enemy and radioactive dust. For the adult population there are gas masks of the GP-5 and GP-7 types, for children aged 1.5 to 17 years - PDF-D (Sh) and PDF-2D (Sh) and for children under the age of 1.5 years - Children's protective cameras KZD-4 and KZD-6.
All civilian gas masks are equipped with a standard gas mask box, which has some distinctive features according to the composition of the filler. Their main difference lies in the design features and sizes of the front parts.
Despite the fact that civilian gas masks are equipped with small-sized boxes containing a small layer of charge, their protective ability against concentrations of chemical agents created in the field is practically unlimited. In emergency situations caused by large-scale emissions of hazardous chemicals, when the ambient air can create concentrations several orders of magnitude higher than those from chemical agents in field conditions, the protective effect time of gas masks is very limited, and in some cases it is zero.
Firstly, this is due to the fact that civilian gas masks do not provide protection against a number of hazardous substances (ammonia, dimethylamine, methyl chloride, nitrogen oxides, ethylene oxide, carbon monoxide and others). Secondly, at short distances from a constantly active source of infection under conditions of high concentrations, an instantaneous leakage of the mixture into the gas box can occur. The protective properties of gas protection boxes against some hazardous chemicals are given in Table. 4.4.3.
In order to expand the range of protection against various hazardous substances and increase protective properties gas masks, the industry currently produces special cartridges DP-1, DP-2, DPG-1, DPG-3 and PZU-K. An additional (hopcalite) cartridge DP-1 (DP-2) is used together with an anti-gas box for protection against carbon monoxide. Additional cartridges DPG-1 and DPG-3 are also used together with a gas mask for protection against ammonia, dimethylamine, nitrobenzene, hydrogen sulfide, carbon disulfide, hydrocyanic acid, tetraethyl lead, phenol, furfural, phosgene, chlorine, hydrogen chloride and ethyl mercaptan. The protective universal cartridge PZU-K provides respiratory protection from both carbon monoxide and a number of hazardous substances. Moreover, it can be used both in conjunction with a civilian gas mask, and only with its front part.
The production of the listed additional cartridges is currently extremely limited due to the lack of funds for their production.
Table 4.4.3
Protective properties of filters civilian gas masks from AHOV 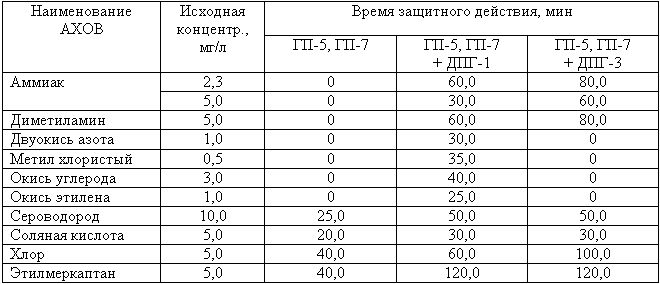
Note. 1. The protective action time is indicated for an air flow rate of 30 l/min, a relative air humidity of 75% and an ambient temperature from -300C to +400C.
2. For children's gas masks, the protective action time against hazardous chemicals (at an air flow rate of 15 l/min) is approximately twice as long as indicated in the table.
Comparison of the data given in table. 4.4.2 and 4.4.3, convincingly shows that the protective properties of industrial gas mask boxes against hazardous chemicals are significantly higher than those of civilian gas mask boxes (without an additional cartridge). Consequently, industrial gas masks can be used in a wider range of concentrations, i.e. it is possible to use them at shorter distances from the source of infection compared to civilian gas masks. The use of civilian gas masks without an additional cartridge is only possible at large distances (hundreds or more meters) from the source of danger.
The use of filter gas masks when performing emergency rescue and other urgent work directly near the site of the spill of hazardous chemicals is unsafe. In these cases, it is recommended to use insulating-type personal respiratory protection equipment.
It is always necessary to assume that a gas mask can be used in emergency only when he is nearby. That is, the gas mask should be stored in close proximity to the workplace or where people are, adjusted in advance and ready for use.
Finding gas masks in warehouses, children's institutions, housing and communal services institutions, etc. in original packaging does not give any reason to assume that the people for whom they are intended are provided with them in case of a sudden emergency.
Insulating gas masks. Insulating gas masks are designed to perform emergency rescue operations in conditions of high concentrations of harmful vapors in the air, when there is insufficient or no oxygen in the air, as well as when working under water. These include gas masks IP-4, IP-4M, IP-4MK for work on land and gas mask IP-5 for work under water. These protective agents work on the basis of chemically bound oxygen. Sodium and potassium superoxide compounds are most widely used as regenerating drugs. All superoxide compounds are characterized by the presence of active oxygen, which is released in molecular form during the reaction of the superoxide with water or carbon dioxide.
All insulating gas masks based on chemically bound oxygen consist of a regenerative cartridge with a trigger device, a breathing bag with an overpressure valve, a front part (has three sizes) with a connecting tube, a frame and a bag with accessories. The regenerative cartridge serves to absorb carbon dioxide and water vapor from the air exhaled by a person and supply oxygen necessary for breathing to the inhaled air. The breathing bag serves as a reservoir for air. It is equipped with an overpressure valve that ensures that the pressure of the air mixture in the breathing bag is maintained not exceeding 40 mm of water. Art. The front part serves to isolate the respiratory organs, eyes and face from the environment and supply air to the respiratory organs from the breathing bag through the regenerative cartridge to the respiratory organs. The frame prevents the breathing bag from being compressed during operation, and also ensures fastening of the regenerative cartridge.
Currently, insulating gas masks and breathing apparatus operating on compressed oxygen (KIP-8, KIP-9) and compressed air (AP-96, AP-98-7K, AP-2000, IVA-24M, ASV-2) are widely used , АВХ-324НТ, etc.).
In the above-mentioned insulating gas masks and breathing apparatus, you can stay in conditions of contamination of the surrounding air with the highest concentrations of chemically hazardous substances. The cost of these gas masks significantly exceeds the cost of filter gas masks. Therefore, according to existing standards, they are provided only to those production personnel at chemically hazardous facilities whose activities are directly related to the performance of work in particularly hazardous areas. These are, first of all, the personnel of gas rescue and dispatch services of chemically hazardous industries and the personnel of formations intended to perform work directly at the site of the spill of hazardous chemicals (scouts, rescuers and liquidators of the consequences of chemical accidents).
Insulating gas masks are reusable. As regenerative cartridges or cylinders are used up, they are replaced with new ones. To use gas masks, advance special training is required for the facility personnel who will be working in them.
Respiratory protective equipment also includes hose-based insulating products that provide the respiratory system with clean air using fans or compressors through connecting hoses. They are used mainly for repairs and cleaning of various containers, basements and other rooms where hazardous chemicals may accumulate.
In addition to insulating gas masks and breathing apparatus, insulating respiratory protective equipment also includes self-rescuers such as SPI-20 and PDU-3, which are used for short-term protection against hazardous chemicals during an emergency exit from a contaminated area. These products also include regenerative cartridges and breathing bags with an overpressure valve. Unlike insulating gas masks, self-rescuers are single-use protective equipment; their use does not present any particular difficulties for untrained personnel.
Dust respirators and simple personal respiratory protection equipment. A respirator is inherently individual remedy protection of respiratory organs from harmful substances contained in the air.
The most widely used dust respirators are the types R-2 (U-2K), "Kama", ShB-1 "Lepestok" and others.
In emergency situations, these respirators can be used to protect the respiratory system from radioactive dust and biological agents.
The simplest RPE includes an anti-dust fabric mask PTM-1 and a cotton-gauze bandage. These products can be used by the public in the same way as dust respirators. They are made either by order of the civil defense authorities in sewing workshops, or by the population themselves according to the samples recommended by the civil defense authorities.
To protect the respiratory system in conditions of chemical contamination, dust respirators and simple personal protective equipment are used only in exceptional cases. For example, when evacuating from a zone of chemical contamination after pre-impregnation with a 5-10% solution of baking soda or a 2% solution of citric acid.
Personal protective equipment for skin
Skin protection means include various products that complement or replace ordinary human clothing and footwear, made from special materials and providing protection of human skin from toxic substances (TS), radioactive dust (RP), biological agents (BS) and hazardous chemical substances .
Skin protection products are divided into classes according to their principle of action, purpose and principle of use. The classification of SZK based on its operating principle is based on the type of material from which the SZK sample is made. In accordance with this principle, all SPS are divided into insulating and filtering.
Insulating protective equipment is made from fabrics with polymer coatings, reinforced and non-reinforced films, and filtering ones are made from air-vapor-permeable fabrics and non-woven materials.
According to their purpose, SZK are divided into combined arms (combined arms skin protection kit, impregnated uniform and kit protective equipment) and special (light protective suit, protective overalls, KIKH-4, KIKH-5, etc.).
According to the principle of use, SPCs are divided into constant wear (combined arms set of protective equipment and impregnated uniforms) and periodic wear, including single use (KZS) and multiple use (light protective suit, combined arms protective kit, FIR, KZS, etc.).
Skin protection products are subject to requirements for protective, operational and ergonomic properties and technical and economic characteristics.
Filter-type SPS must provide protection from pulses of light radiation nuclear explosion(SIYV), vapors and aerosols of chemical agents, BS, RP and hazardous chemicals.
An insulating-type SPS in combination with a filter-type SPS must exclude human injury from small drops of OM type VX, vapors, aerosols and drops of mustard gas, soman and hazardous chemicals, aerosols of BS, RP and SIYV. Compliance with the requirements for protection from hazardous agents practically solves the issue of protection from radioactive dust and bacterial aerosols.
Insulating-type protective equipment must, in addition, protect uniforms from contamination by droplet-liquid agents, BS and RP.
To equip troops and rescue units civil defense Skin protection equipment includes the combined arms protective kit (OZK), light protective suit (L-1) and protective filter clothing (PFC).
OZK is intended for repeated protection of human skin, uniforms, equipment and individual weapons from chemical agents, BS, RP, and hazardous chemicals.
The kit includes a protective raincoat, stockings, and gloves. The protective raincoat with sleeves and hood is made in five sizes: the first is for a person’s height up to 165 cm, the second is from 166 to 170 cm, the third is from 171 to 175 cm, the fourth is from 176 to 180 cm, the fifth is from 181 cm and above.
Protective stockings have three sizes: the first - for boots of size 37-40, the second - 41-42, the third - 43 sizes and above.
L-1 is intended for reusable use to protect human skin and uniforms from chemical agents, BS, RP and hazardous chemicals.. It is special means protection and is used during long-term work in contaminated areas, as well as when performing decontamination, decontamination, rescue and other urgent work.
The set includes a jacket with a hood, trousers with stockings, two pairs of gloves, an impregnated balaclava and a carrying bag.
The L-1 suit is available in three sizes: the first - for a person’s height up to 165 cm, the second - from 166 to 172 cm, the third - above 172 cm.
ZFO is intended to protect the skin from exposure agents, RP and BS. The kit includes an impregnated protective filtering overall made of moleskin, worn over non-impregnated underwear, a cotton balaclava, two pairs of foot wraps, one of which is impregnated, rubber gloves and protective rubber boots.
To impregnate overalls and foot wraps, an absorption-type formulation is used based on K-4 paste, consisting of alkylphenol, chlorinated paraffin and the OP-10 preparation in a ratio of 1.5: 1.5: 1.0 by weight.
To increase the protective properties of this clothing, waterproof raincoats and capes, mittens and boots are used over it.
Recommendations for the use of personal protective equipment
Based on the levels of damaging factors in the conditions of the release of hazardous chemicals, the territory around a chemically hazardous facility can be conditionally considered in the form of three danger zones, each of which is determined by the damaging concentrations of hazardous chemicals, the time of their exposure, as well as the presence of their liquid phase and an open fire flame.
First zone- the most dangerous from the point of view of increased concentrations of hazardous substances, contact with the liquid phase and exposure to open flame during fires. Based on the distance from the source of infection, removing the outer border of the zone, its depth can be up to 250 m.
Second zone a - less dangerous, the concentration of hazardous substances is approximately two to three orders of magnitude lower than the maximum possible, the effects of the liquid phase and fire are unlikely. The depth of this zone can be 250-1000 m.
In the third zone danger, the concentration of hazardous substances is four to five orders of magnitude lower than the maximum possible. Its distance from the source of infection can be more than 1000 m.
Exposure to maximum and relatively high concentrations of hazardous chemicals is most likely in the first danger zone. Here, exposure to both the liquid phase of a toxic substance and high concentrations is possible. In this regard, in this area, production personnel and personnel of formations involved in the work to eliminate the consequences of the accident must use insulating respiratory and skin protective equipment. Evacuation of production personnel from a hazardous area is possible with the use of industrial gas masks.
In the second danger zone, where exposure to concentrations is likely to be significantly lower than in the first zone and where exposure to hazardous chemicals in a droplet-liquid state is unlikely, protection of personnel of the formations can only be carried out using personal respiratory protection equipment - industrial gas masks. Moreover, the latter must be under constant control to determine the time of processing of the charge. The use of skin protection products in this area is necessary only if there is a resorptive effect of toxic chemical vapors in the atmosphere.
In the third danger zone, relatively low concentrations of hazardous substances should be expected. Therefore, it is possible to use civilian gas masks to evacuate people to safe areas. But at the same time, they must provide protection from dangerous substance, otherwise their use is only possible with additional cartridges.
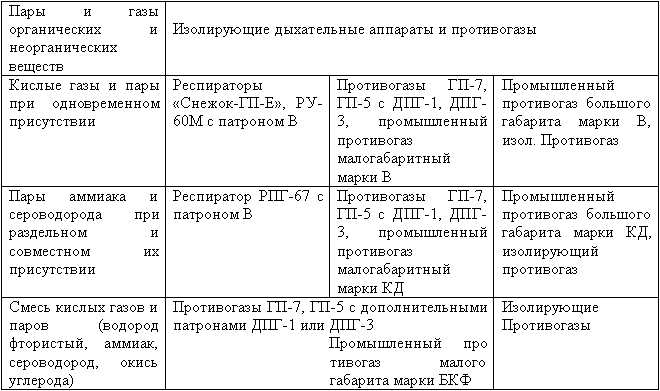
Note: Children's gas masks are used in the same way as GP-7 and GP-5.
The population that lives near a chemically hazardous facility may be exposed mainly to hazardous chemicals characteristic of the third danger zone (gas, hazardous chemical vapors) and only partially to the second zone (gas, hazardous hazardous chemical vapors in relatively high concentrations - 8-10 mg/l) . The time spent in the contaminated zone is determined by the duration of evacuation measures. According to this, special protection There is no point in considering the skin exposure to hazardous chemicals for the population.
In conclusion, it is necessary to emphasize once again that the presence of a gas mask at the place of average daily stay of people does not mean that its owner is ensured safety from damage to hazardous substances or hazardous agents in an emergency situation. The gas mask must be fitted in advance and stored in accordance with the requirements.
The fitting of gas masks in military conditions is carried out with mandatory testing indoors using chemical agent simulators (chloropicrin or other substances). It is quite difficult to check the correct fit of gas masks among the population, as organizationally it should be carried out in a specially designated place under the supervision of instructors.
Task federal bodies executive power, executive authorities of the subjects Russian Federation, local self-government, and government emergency response bodies to ensure the accumulation of the required amount of personal protective equipment and the timely distribution of them to the population in the event of emergency situations.
- Abstract: Elementary particles
- Presentation on the topic "management"
- History of the development of computer technology presentation for a lesson on the topic Historical development of computer technology presentation
- Astronomy Presentations Interesting Topics for Astronomy Presentations
- Presentation on history "counting years in history"
- Astronomy Presentations Astronomy Presentation Template
- The anniversary of the expulsion of the Karachais recalled the problem of rehabilitation of repressed peoples
- Udmurt people What peoples live on the territory of Udmurtia
- Russia is a multinational state We live in a multinational country
- The smallest peoples of the world Which group of peoples is the smallest
- How to change a cash receipt order in 1c
- Day of Remembrance of Fallen Russian Internal Affairs Officers Heroism of Police Officers
- Northern coast of Neva Bay
- Enviable beauties in politics (17 photos)
- The best ballet performances
- Biography, political activity
- The magical world of crystals
- How to salt milk mushrooms: a quick recipe
- Ten Surprisingly Profitable Illegal Trades
- Management project based on the example of an enterprise presentation









