"Individual medical protective equipment
State budgetary educational institution of higher professional education "Orenburg State Medical Academy of the Federal Agency for
Department of Disaster Medicine
TOOLKIT
for students on the course "Life Safety"
Topic number 7:"Personal medical equipment".
Orenburg - 2012
Personal protective equipment classification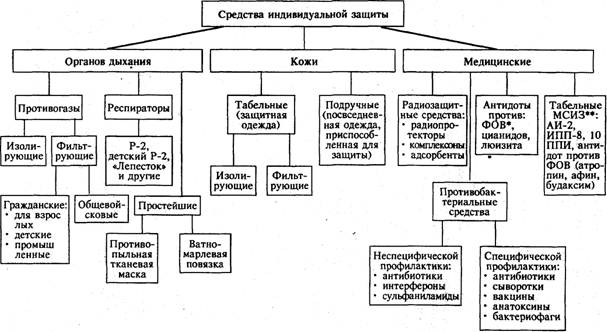
The effectiveness of protecting the population and rescuers in emergency situations (ES) is achieved by using various organizational, engineering and special (including medical) measures, taking into account the peculiarities of the impact of the damaging factor of emergencies. At the same time, medical protection measures are carried out in almost all emergencies.
Medical protection- a set of measures carried out (organized) by the disaster medicine service and the civil defense medical service (MSGS) to prevent or minimize the impact of damaging factors on the population and rescuers. Medical protection is an integral part of health care.
Medical protection measures include:
assistance in the provision of individual means of prevention of lesions (antidotes, radioprotectors, means of special treatment, etc.), medicines for first aid, as well as participation in training in the rules and techniques for using them ;
Conducting sanitary and hygienic and anti-epidemic measures to prevent or reduce the negative impact of the damaging factors of emergencies;
Development (based on an assessment of the situation in an emergency) and implementation of a set of measures for the medical protection of the population and rescuers;
Participation in the psychological training of the population and rescuers;
Organization and observance of the sanitary regime at the stages of medical evacuation, control of radioactive and chemical contamination of the injured (sick) and rescuers, as well as the implementation of other protective measures in the formations and institutions of the All-Russian Disaster Medicine Service and MSGD.
Personal medical protective equipment (IMSZ).
Under medical protection it should be understood as medicines and medical property intended for the implementation of measures to protect the population and rescuers from the impact of adverse factors of emergency.
Medical personal protective equipment (MSIZ) is intended for the prevention and provision of medical assistance to the population and rescuers who have suffered (found themselves in the zone) from the damaging factors of emergencies of a radiation, chemical or biological (bacteriological) nature.
There is no one-size-fits-all ISIZ. In each specific case, it is necessary to find the most effective means that could prevent or weaken the impact of the damaging factor. The search for such means and their introduction into practice is associated with a comprehensive study of pharmacological properties, with special attention being paid to the absence of undesirable side effects, the effectiveness of protective properties, the possibility applications with massive losses.
The main requirements for the MSIZ of the population and rescuers in emergencies are:
The possibility of their early application before the onset of exposure to damaging factors;
Simple methods of application and the possibility of storage by the population and rescuers;
The effectiveness of the protective action;
Elimination of adverse consequences of the use by the population and rescuers (including unreasonable);
Favorable economic characteristics (low cost of production, rather long shelf life, the possibility of subsequent use in health care practice when refreshing the created stocks, the possibility of production to fully provide the population and rescuers with them).
According to their purpose, MSIZ are subdivided into:
Used in radiation accidents;
Used in chemical accidents and domestic poisoning with various toxic substances;
Used for the prevention of infectious diseases and weakening the damaging effects of toxins on the body;
Providing the most effective partial special treatment in order to remove radioactive, chemical substances, bacterial agents from human skin.
The ISIZ includes; radioprotectors (radioprotective drugs), antidotes (means of protection against exposure to 0V and AOXV), antibacterial agents (antibiotics, sulfonamides, vaccines, serums) and special treatment agents.
Medical Radiation Protection Equipment are subdivided into three groups.
Means for the prevention of radiation injuries during external irradiation.
To weaken the body's reaction to the effects of ionizing radiation, medications are used, which are usually called radioprotective drugs, or radioprotectors. These are drugs that cause hypoxia in radiosensitive tissues and thereby reduce their radiosensitivity (cystamine, indralin, etc.), as well as hormonal agents (diethylstilbestrol, etc.). Radioprotectors act only when administered before irradiation and in large doses (unsafe for the body),
Cystamine belongs to sulfur-containing drugs and is a disulfide of a hydrochloric salt - mercaptoethylamine. The recommended dose is 1.2 g. The optimal period of use of cystamine is 40-60 minutes before exposure to ionizing radiation, the duration of the radioprotective effect is 4-5 hours.
Indralin is a heterocyclic compound (derivative of in-dolylalkylamine) and belongs to emergency radioprotectants. The recommended human dose is 0.45 g per dose. Three 0.15 g radioprotectant tablets are thoroughly chewed and washed down with water. The optimal admission period is 15 minutes before the expected exposure. The drug provides protection for 1 hour. It can be taken again with an interval of 1 hour.
The radioprotective effect of indralin manifests itself, as a rule, with short-term exposure to ionizing radiation of various types (gamma radiation, high-energy neutrons, protons, electrons) with a high dose rate. The effectiveness of its use increases in conditions of uneven irradiation and when combined with the means of early and complex treatment of radiation injuries. Indralin retains antiradiation activity when the body is exposed to such extreme factors as physical activity, elevated air temperature and others, as well as when used together with other medical means of anti-radiation protection, in particular with means of preventing a primary reaction to radiation. The drug does not adversely affect the operator's room and other types of professional activities of Specialists of various profiles and is well tolerated by them in extreme conditions.
When personnel carry out emergency work under conditions of exposure to low-intensity γ-radiation on a radioactively contaminated area with radiation doses of 150-200 mSv, first of all, substrate therapy means are prescribed, which contribute to the acceleration of post-radiation reparative processes in the body. For this purpose, it is possible to use riboxin, aminotetravit, tetrafolevite and preparations with succinic acid. Currently, a new anti-radiation drug, indometaphen, has been developed, intended to protect personnel from low-intensity γ-radiation, primarily from radiation damage to the hematopoietic system.
Means of preventing or weakening the primary general reaction of the body to radiation(nausea, vomiting, general weakness). These include mainly sedatives - dimetcarb (includes 0.04 g of the antiemetic drug dimetpramide and 0.002 g of the psychostimulant sydnocarb), etaperazine, aeron, dimetpramide, diethylperazine, raglan, cerucal, dinelfen (dimetpramide, caffeine and ephedrine); an effective antiemetic agent is currently being produced - latran (0.008 g).
Means for the prevention of radiation injuries during the incorporation of radionuclides(when RV is received through the mouth or by inhalation). To accelerate their removal from the gastrointestinal tract and prevent absorption into the blood, adsorbents are used. Unfortunately, adsorbents do not have a polyvalent effect; therefore, adsorbar, polysantimine, highly oxidized cellulose, and algisorb are used to remove strontium and barium isotopes; with the incorporation of plutonium, inhalation of the pentacin preparation; if radioactive iodine gets in, stable iodine preparations; to prevent the absorption of cesium isotopes, ferrocin, bentonite clay, vermiculite, Prussian blue are most effective.
Like pentacin, zincacin binds to stable water-soluble complexes isotopes of plutonium, americium, yttrium, cerium, promethium, etc.
Cation and anion exchange resins, emetics, gastric lavage, expectorants (with inhalation of radioactive substances), chelating agents (drugs that accelerate the excretion of radioactive substances from the body: citric, lactic, acetic acids) can be administered internally. Complexons are used inhalation in the form of aerosols and form complex compounds with radioisotopes in the lungs, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream and excreted in the urine. Along with complexones, unitiol is used to remove uranium and polonium salts from the body.
Many medicines are not only means of medical protection, but to a greater extent - means of providing medical care and treatment of radiation injuries, namely:
Adaptogens (increase the general resistance of the body) - preparations of Eleuterococcus, ginseng, Chinese magnolia vine; dibazol; bee venom (bee venom polypeptide - mellitin); snake poison; shellfish (mussel) extracts;
Hematopoietic stimulants - pentoxil, hemostimulin, etc.;
Central nervous system stimulants - endopam, bemegrid, other neuroleptics, tranquilizers, antidepressants, psychotropic drugs;
Antihemorrhagic agents - serotonin, mexamine, cystamine (in combination with other drugs), bathylol, tezan liniment (for local application of radiation burns of the skin), etc.
Medicines for the prevention and treatment of radiation injuries are used as prescribed by a doctor, and only those medicines that are contained in an individual first-aid kit can be used by the population independently.
There are means of preventing radiation damage to the skin when it is contaminated with radioactive dust. The most effective measure in this case is sanitization as soon as possible after contamination (washing with water and soap, it is advisable to use the drug "Protection" and 1-3% solution of hydrochloric acid or sodium citrate).
Antidotes(antidotes) are medicinal means of anti-chemical protection capable of neutralizing poison in the body by physical or chemical interaction with it or providing antagonism with poison when acting on enzymes and receptors.
The most important condition for obtaining the maximum therapeutic effect from antidotes is their earliest use.
There are no universal antidotes. There are antidotes for organophosphorus toxic substances (OPT): anticholinergics - atropine, athen, budaxim, tarren, aprofen and others, cholinesterase reactivators - dipiroxime, isonitrosine, toxogonin, etc. Antidotes for cyanides are amyl nitrite, sodium propyl nitrite, antidotes for cyanides. For lewisite and other arsenic-containing poisons, unitiol or BAL is the antidote. In case of BZ poisoning, triftazine, galantamine, bugafen are used. The antidote for lesions with irritating substances (adamsit, chloroacetophenone, C5, SK) is ficilin, as well as an anti-smoke mixture.
In emergency situations of a chemical nature, antidotes should be applied immediately after exposure to 0V. Prophylactic antidotes for OPA (P-10M) and carbon monoxide (amizil) should be applied immediately before entering the accident site. The most effective antidotes can be when they are administered intramuscularly, subcutaneously, intravenously. Obviously, with a massive defeat of the population, and even more so in a very limited time, this is extremely difficult to do.
Antidotes for self-use by the population are produced in tablets and used in accordance with the attached instructions.
Antibacterial agents are subdivided into means of emergency nonspecific and specific prophylaxis. The means of non-specific prophylaxis include broad-spectrum antibiotics and sulfonamides, as well as interferons. To the means of specific prophylaxis - antibiotics of a narrow spectrum of action, serums, vaccines, toxoids, bacteriophages.
Some of these funds are invested in a personal first aid kit.
To the official IMSZ include an individual first-aid kit (AI-2), an individual anti-chemical package (IPP-11), an individual dressing package (PPI) and an antidote for self - and mutual aid for FOV in syringe tubes (atropine, athens, budaxim).
The composition of first-aid kits may vary depending on the availability of antidotes and on the purpose (for military personnel in a local or large-scale war; rescuers in accidents in peacetime or wartime, etc.).
Individual first aid kit AI-2 is designed to prevent or reduce the effect of various damaging factors, as well as to prevent the development of shock in traumatic injuries.
The contents of the first-aid kit are made up of a syringe-tube and canisters with medicines differing in shape and color, placed in a plastic case and held by the internal partitions of the body. Each medicine is in a strictly defined place, which allows you to quickly find the necessary remedy.In the cold season, it is recommended to store the first-aid kit in a breast pocket to prevent liquid dosage forms from freezing.
The medicines contained in the first-aid kit are used depending on the situation, both at the direction of the medical worker (commander, work manager), and independently in accordance with the instructions included in the first-aid kit, which the population and rescuers get acquainted with during the training process.
It is necessary to strictly observe the established dosages of drugs in order to avoid a decrease in their effectiveness or, conversely, the manifestation of the negative effects of an overdose.
In the nest No. 1 of the first-aid kit there is a syringe-tube with 2% solution of promedol. Promedol is a powerful pain reliever. It is used to prevent shock in case of severe pain caused by fractures, extensive wounds, crushing of tissues and burns. When using a syringe tube, you must:
Remove the syringe tube from the first aid kit;
With one hand, grasp the ribbed rim of the cannula, with the other - for the body and turn it clockwise until the membrane is punctured;
Holding the syringe tube by the cannula, remove the cap that protects the needle;
Holding the syringe tube by the ribbed rim of the cannula and not squeezing the body with your fingers, insert the needle into the soft tissues of the thigh, buttocks or shoulder (you can through clothing) up to the cannula;
Squeeze out the contents of the tube by squeezing its body;
Without unclenching your fingers, remove the needle .
After the introduction of its contents to the patient, the syringe tube must be attached to a bandage or clothing in a conspicuous place.
In the nest. No. 2 there is a round red pencil case with a prophylactic antidote for FOV - taren (6 tab.). One tablet is taken on command. If signs of poisoning appear, you must take another pill yourself. The drug can be taken again no earlier than after 5-6 hours.
In nest No. 3 there is a long round pencil case without coloring with antimicrobial agent No. 2. The pencil case contains 15 tabs. sulfadimethoxine (long-acting sulfa drug). It is taken in case of gastrointestinal disorders after radiation, with injuries and burns in order to prevent infection. On the 1st day, 7 tablets are taken, in the next two, days - 4 tablets. in a day.
In the nest No. 4 there are two octahedral pink pencil cases containing the radioprotective agent No. 1 - cystamine (1 tab. In each). 30-60 minutes before entering the contaminated area should be taken b tab. If necessary, repeated admission is allowed after 4-5 hours.
In nest No. 5 there are two unpainted tetrahedral pencil cases with anti-bacterial agent No. 1, 5 tabs each. in everyone. Chlortet-racycline is used as a means of emergency nonspecific prophylaxis of infectious diseases. The drug is taken with the threat of bacterial infection, as well as with extensive wounds and burns in order to prevent purulent complications. The first reception is 5 tab. again (after 6 hours) another 5. Biseptol or septrin can be used, as well as any modern antibiotics (ampicillin, kefzol, cefobid, digital, etc.).
In nest No. 6 there is a white tetrahedral pencil case containing radiation protective agent No. 2 - potassium iodide (10 tab. 0.25 g each). Adults and children from two years of age and older take the drug at 0.125 g, that is, 1/2 tab. once a day within 7 days from the moment of radioactive fallout (children under two years old take 0.04 g per day) after meals, washed down with jelly, tea or water. For pregnant women, the intake of potassium iodide (0.125 g each) must be combined with the simultaneous intake of potassium perchlorate - 0.75 g (3 tabs, 0.25 g each).
In the absence of potassium iodide, a 5% tincture of iodine is used, which is given to adults and adolescents over 14 years old at 44 drops 1 time a day or 20-22 drops 2 times a day after meals for 1/2 glass of milk or water. For children 5-14 years old, 5% iodine tincture is prescribed 20-22 drops 1 time a day or 10-11 drops 2 times a day after meals for 1/2 glass of milk or water. For children under 5 years of age, tincture of iodine is not prescribed internally, and an alcoholic solution of iodine is applied only to the skin: 10-20 drops, applied in the form of a mesh on the skin of the thigh or forearm.
A fairly quick effect is also given by lubricating the skin with tincture of iodine anywhere (the area of the treated surface is 2x5 cm).
A delay in taking iodine preparations leads to a decrease in its protective effect. So, if they are taken 2-3 hours after the beginning of the intake of radioactive iodine into the body, the effectiveness of the drugs decreases by 25-30%, and after 5-6 hours - by 50%. At a later date, the use of iodine preparations is ineffective. Timely taken iodine preparations prevent the accumulation of the radioactive isotope of iodine in the thyroid gland, therefore, prevent its defeat.
In nest 7 there is a blue round pencil case, which contains one of the antiemetics - latran, dimetramide or etaperazine (5 tab.). The drug is taken in 1 tab. immediately after irradiation, as well as when nausea, vomiting occurs both after irradiation and after contusion, with concussion. With continued nausea, ztaperein should be taken repeatedly, 1 tab. - after 3-4 hours
Children under 8 years old, when taking all drugs from AI-2, are given 1/4 tab at one time. (except for potassium iodide), from 8 to 15 years old - 1/2 tab. An exception is an anti-bacterial agent, which is used in full dose in children over 8 years old, and not used for up to two years.
In an individual first aid kit there are no general calming agents and agents that weaken the feeling of fear. In an emergency, as practice has shown, these funds are necessary. Therefore, it is possible to recommend to the population, in addition to the content of AI-2, to use tranquilizers (such as Elenium, Sibazon, Fenozepam).
Individual first aid kit AI-4
Designed to replace AI-2. Contains a complex of drugs necessary to protect the population. AI-4 is intended for carrying out first aid measures in the order of self and mutual assistance, prevention and weakening of the damaging effect of radioactive substances (RS), bacterial agents (BS), organophosphate substances (OPO) and toxic substances (AOKhV).
Package 1.
1. Anti-pain agent.
3. Remedy for OP poisoning.
4. Radioprotective agent No. 1.
5. Radioprotective agent No. 2.
6. Antibacterial agent No. 1.
7. Antibacterial agent No. 2.
8. Antiemetic.
9. Reserve antidote of OPF.
Package contents 2.
1. Anti-pain agent.
2. A remedy for AOXV poisoning.
3. Radioprotective agent No. 1.
4. Radioprotective agent No. 2.
5. Antibacterial agent No. 1.
6. Antibacterial agent No. 2.
7. Antiemetic.
8. Reserve antidote of OPF.
Package contents 3.
1. Anti-pain agent.
2. Remedy for OP poisoning.
3. Radioprotective agent No. 2.
4. Antibacterial agent No. 1.
5. Antibacterial agent No. 2.
6. Antiemetic.
7. Reserve antidote OPF.
Individual anti-chemical package(IPP-11) is intended for partial special treatment in order to neutralize organophosphate AOKhV and 0V, as well as toxins of skin blistering action on open areas of the skin, clothing and PPE.
IPP-11 is a sealed bag containing napkins moistened with the same liquid. Its use allows for a more targeted and economical use of the product.
In the absence of an individual anti-chemical package, partial special treatment can be carried out with 5% ammonia solution, 1.0% chloramine solution, chlorizalde milk and other means.
Individual dressing package(PPI) - intended for the application of a primary aseptic dressing on a wound, burn surface. It contains a special dressing material, which is enclosed in two shells: the outer one is made of rubberized fabric with a description of the opening and use method printed on it, and the inner one is made of paper.
There is a safety pin in the fold of the inner shell. The casings ensure the sterility of the dressing material, protect it from mechanical damage, dampness and contamination. The material in the bag consists of a gauze bandage 10 cm wide and 7 m long, two cotton-gauze pads of equal size 17x32 cm in size. One of the pads is sewn to the bandage, the other is connected to it movably and can move freely along the length of the bandage.
In the event of a chest injury, when a foamy, bloody fluid is released from the wound, or air intake is audible during inhalation (open pneumothorax), an occlusive (sealing) dressing is applied to the wound. For this, a rubberized sheath is used, which is directly applied to the wound with the inside, covered with pads and tightly bandaged.
A developing area of medical protection of the population and rescuers in emergencies is the search and use of medical protection equipment in case of adverse effects on the body of physical factors, as well as their combination with chemical and other factors that occur in emergencies.
As an ISIZ from adverse effects of elevated temperature when carrying out emergency rescue operations, medicinal products are used thermoprotective drugs.
Medicines are known that increase the passive resistance of the body to the action of high ambient temperatures (decrease in stressful emotional-behavioral reaction, limitation of motor activity and oxygen consumption by tissues, increased evaporative heat transfer, etc.). However, the most effective drugs used by participants in the elimination of emergencies in conditions of elevated temperature (including when using isolating means of protecting the skin and respiratory organs) are those that could ensure the required level of performance for a sufficient time, and prevent severe hyperthermia outcomes.
Preferred thermoprotectors in conditions of limited evaporative heat transfer, as well as when it is necessary to perform significant amounts of physical work, are drugs with moderate hypothermic and cardiostimulating action, which have antihypoxic activity. Such requirements are met by the preparations bemitil, bromantane and especially their combination.
Domestic and foreign researchers are actively searching for drugs, increasing the cold resistance of the body - frigoprotectors.
Currently, there are three main ways of pharmacological correction of conditions associated with hypothermia. The first and most common is associated with increased heat production due to the calorigenic effect of catecholamines. The second is aimed at regulating energy supply systems, and the third is aimed at reducing energy consumption and the subjective feeling of cold through the use of drugs that significantly reduce muscle activity and block the body's sensitivity to hypothermia. The representative of the first way of regulation is sydnocarb with glutamic acid, the second - yakton (succinic salt of tonibralic acid) and the third - the combination of diazepam with sodium oxybutyrate.
Of great interest are drugs from the group actoprotectors and anti-hypoxants, the biological action of which is based on the optimization of systemic and cellular metabolic reactions, adequate to the intensity of the acting factor.
When performing physical work in the cold, sydnocarb (10 mg) in combination with yakton (400 mg) or bemytil (250 mg) has the most favorable effect on the functional state of the body. These drugs improve the thermal state of the "shell" of the body, eliminate microcirculation disorders, restore the reaction of the cardiovascular system to physical activity, and stimulate aerobic processes. The use of bromantane (100 mg) stabilizes the state of the deep structures of the "core" of the body and thus has a frigoprotective effect.
Currently, studies are underway to find the possibility of using pharmacological agents. to prevent the adverse effects of noise on the human body. According to research data, antihypoxant olifen, actrprotecto bemitil and nootropic cavinton are drugs that increase a person's resistance to impulse noise and maintain performance.
Due to the fact that toxic substances of various types of action are found in the accident zone, the search for pharmacological drugs that affect the general mechanisms of toxicity or optimize the functioning of the natural pathways of detoxification in the body is of increasing interest.
Pharmacological means of correcting disorders caused by various toxic substances can be drugs with certain properties, in particular, increasing the efficiency of the functioning of natural detoxification mechanisms. Currently, the prospects for research and the possibility of creating preparations with universal protective properties confirmed by experimental data. The so-called "group" antidotes "can probably be pharmacological agents that have a wide spectrum of action with antihypoxic and antioxidant properties, or are metabolic substrates of the main bioenergetic processes. The necessary initial data were obtained on the real possibility of creating such a universal drug based on aszazol, which turned out to be effective in poisoning with nitrogen dioxide, sodium nitrite, in hemolytic manifestations, toxic damage to microphage cells, that is, in poisoning with a number of toxic substances.
Prospective is the search for drugs that increase human resistance to the combined effects of adverse factors of different nature, characteristic of emergencies. Chemical and physical factors can cause a number of universal pathological changes, such as the development of hypoxia, impaired energy production, activation of lipid peroxidation of cell membranes. This makes it possible to use drugs from various classes, but with a wide spectrum of pharmacological activity to maintain stability and performance when exposed to toxic substances and physical factors.
Currently, drugs have been created that have a wide spectrum of action, which makes it possible to use them as means of protection in emergency situations. Preparations developed bromoithane and bromytyl, which can be used as prophylactic agents to increase the stability of the human body to the effects of various chemicals, high and low air temperatures, as well as impulse noise. The development of a recipe with a conventional name is almost close to completion "Phenazel", which, in terms of its effectiveness, the value of the protective index, surpasses the antidote of carbon monoxide acisol and has protective properties against other factors, in particular, a thermoprotective effect. Successful completion of these studies will put into the hands of doctors effective medicines to fight for the life and health of liquidators of emergency situations accompanied by fires. The problem of increasing the protective properties of the body by improving the MSIZ used in emergency situations needs further development. We need more effective radioprotective drugs, antidotes and antimicrobial drugs, better forms and methods of their use, wider possibilities of their production in the country and use for preventive purposes by the population and rescuers.
The procedure for providing, accumulating, storing and issuing personal protective equipment.
Stocks of PPE to provide workers and employees at economic facilities are equipped with new gas masks at the expense of facilities. The accumulation of children's gas masks is organized in children's institutions.
For the entire population living in the territory adjacent to the nuclear power plant (in the 30-kilometer zone), stocks of iodine preparations are being created. A very important measure is the organization of the proper storage of PPE. Their storage places should be as close as possible to workplaces, as well as residential areas. If necessary, the issuance of PPE should be provided as soon as possible. The most convenient is the creation of special warehouses of GO property in each workshop (department). If this is not possible, then during storage at the factory warehouse, this property should be grouped by workshops (departments), and in each workshop - by shifts and teams. Storage conditions must meet the relevant requirements, ensure the technical serviceability of the property (dry unheated rooms with ventilation, containers - standard boxes).
The storage of PPE for the non-working population is carried out at the place of residence. The following storage periods have been established: for children's gas masks - 10 years; for gas masks of the IP-46 and GP-5 type - 5 years; for respirators and skin protection equipment made of rubberized fabric - 3 years; for individual first-aid kits AI-2 - no more than 4 years. After the expiration of the shelf life, the shelf life is determined annually (laboratory control).
In peacetime, gas masks are stored disassembled: filter-absorbing boxes, sealed with a rubber stopper and a cap, are placed on the bottom of the box, gas masks are placed on the boxes, and rubber face pieces are placed on top of them.
For issuing PPE pick-up points are organized at the rate of one point for 2000 employees. In 1 hour, such a point is capable of preparing and issuing PPE to 180-200 people.
In the absence of gas masks at the facilities, gas masks and respirators designed to protect against harmful gases emitted during some production processes at enterprises (industrial gas masks), as well as anti-dust fabric masks (PTM-1), can be used to protect the respiratory system.
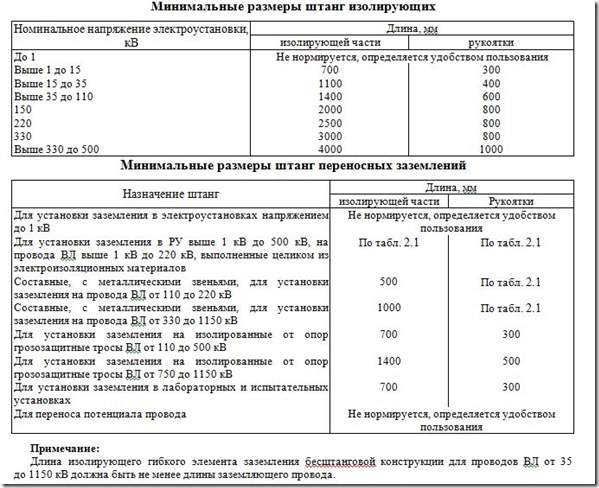
- Rules for the use of electrical protective equipment when carrying out work in electrical installations
- How to sew fleece mittens
- Protective equipment in electrical installations
- Computer glasses: which is better to choose
- How to wash clothes with Thinsulate insulation
- Training in electrical safety, labor protection, ecology, electrical safety, fire-technical minimum, first aid to victims of the courses
- Protective equipment in electrical installations up to and above 1000 Volts
- What is fleece fabric, where is it used and how to care for it
- Personal protective equipment
- What is this fabric?
- Thinsulate
- Eminem (Marshall Bruce Mathers III) - biography, family and personal life of the rapper
- Directions and styles of jazz Jazz history of origin and development
- Deniskins 'stories of the dragoon Read the dragoons' stories of the dragoons in full
- Deniskin's stories by Viktor Dragunsky: everything about the book Deniskin's stories list
- Castes in India - how does the division take place?
- Muslim Magomayev: biography, creativity, career, personal life
- The peoples inhabiting their country
- Largest ethnic groups and small peoples
- Interesting facts from the life of Leo Nikolaevich Tolstoy