Protective equipment in electrical installations. A common part.
Good time of the day, dear friends.
With this article, I begin a cycle about an extremely important sector of the electrical laboratory. Namely, about testing protective equipment. Today, let's say, is the introductory part.
Protective equipment used in electrical installations must meet the requirements of the relevant state standards.
When working in electrical installations, the following are used:
- means of protection against electric shock (electrical protective equipment);
- means of protection against electric fields of increased intensity, collective and individual (in electrical installations with a voltage of 330 kV and above);
- personal protective equipment (PPE) in accordance with the state standard (protective equipment for the head, eyes and face, hands, respiratory system, from falling from a height, special protective clothing).
In this series of articles, we will mainly talk about means of protection against electric shock.
Now I will give a number of concepts and definitions.
Electrical protective equipment - means of protection against electric shock, designed to ensure electrical safety.
The main insulating electrical protective agent - an insulating electrical protective device, the insulation of which can withstand the operating voltage of the electrical installation for a long time and which allows you to work on live parts that are energized.
Additional insulating electrical protective equipment - an insulating electrical protective device, which in itself cannot provide protection against electric shock at a given voltage, but complements the main protection means, and also serves to protect against touch voltage and step voltage.
Contact voltage - voltage between two conductive parts or between a conductive part and earth when a person touches them at the same time.
Step voltage - voltage between two points on the surface of the earth, at a distance of 1 m from one another, which is taken equal to the length of a person's step.
Safe distance - the smallest permissible distance between the worker and the source of danger, necessary to ensure the safety of the worker.
Voltage indicator - a device for determining the presence or absence of voltage on live parts of electrical installations. In installations up to 1000V, it is called a low voltage indicator (UNV), in installations above 1000V - a high voltage indicator (HVN).
Voltage presence indicator - a device for warning personnel about being in a potentially hazardous area due to approaching live parts that are energized at a dangerous distance or for a preliminary (approximate) assessment of the presence of voltage on live parts of electrical installations at distances between them and operating, significantly exceeding the safe ones.
Voltage-free operation - work performed with touching live parts that are energized (working or induced), or at distances from these live parts less than permissible.
Security poster (sign) - color graphic image of a certain geometric shape using signal and contrast colors, graphic symbols and (or) explanatory inscriptions, designed to warn people about an imminent or possible danger, prohibition, prescription or permission of certain actions, as well as information about the location of objects and means, use which eliminates or reduces the impact of hazardous and (or) harmful factors. Posters are divided into 4 groups
Banning posters (1 group)
Warning signs and posters (group 2)
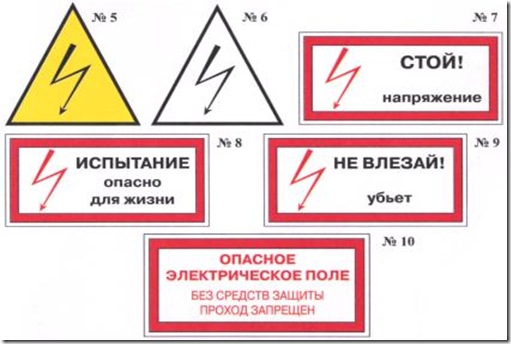
Prescribing posters (group 3) more often the frame on the poster is green
Index poster (group 4)

Electrical protective equipment includes:
- insulating pliers;
- voltage indicators;
- signaling devices of voltage presence, individual and stationary;
- devices and devices for ensuring the safety of work during measurements and tests in electrical installations (voltage indicators for checking the phase coincidence, electric measuring tongs, devices for cable puncture);
- dielectric gloves, galoshes, boots;
- protective fences (shields and screens);
- insulating pads and caps;
- manual insulating tool;
- portable grounding;
- posters and safety signs;
- special protective equipment, insulating devices and devices for work under voltage in electrical installations with a voltage of 110 kV and above;
- flexible insulating coatings and linings for work under voltage in electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V;
- Insulating fiberglass ladders and step-ladders.
Insulating electrical protective equipment is divided into basic and additional.
The main insulating electrical protective equipment for electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V include:
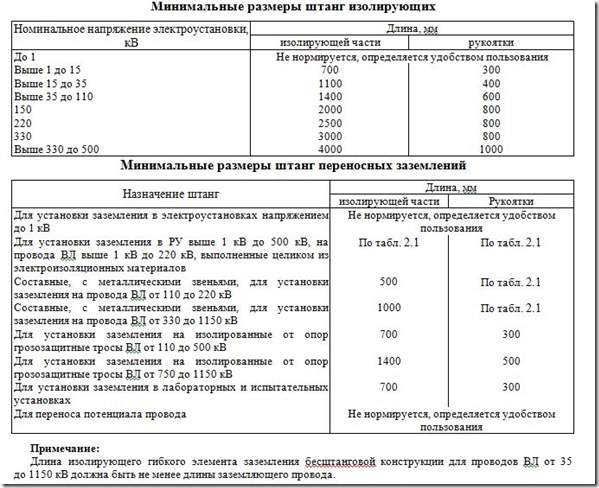
- insulating rods of all types;
- insulating pliers;
- voltage indicators;
- devices and devices for ensuring the safety of work during measurements and tests in electrical installations (voltage indicators for checking the phase coincidence, electric measuring tongs, devices for cable puncture, etc.);
- special means of protection, devices and insulating devices for work under voltage in electrical installations with a voltage of 110 kV and above (except for rods for transfer and equalization of potential).
Additional insulating electrical protective equipment for electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V include:
- dielectric gloves and boots;
- dielectric carpets and insulating supports;
- insulating caps and linings;
- rods for transfer and potential equalization;
The main insulating electrical protective equipment for electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V includes:
- insulating rods of all types;
- insulating pliers;
- voltage indicators;
- electrical clamps;
- dielectric gloves;
- manual insulating tool.
Additional insulating electrical protective equipment for electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V includes:
- dielectric galoshes;
- dielectric carpets and insulating supports;
- insulating caps, coatings and linings;
- attached ladders, insulating fiberglass ladders.
It should be noted that some funds, being basic in electrical installations up to 1000V, become additional in electrical installations above 1000V, and some, for example, rugs are always additional.
PROCEDURE AND GENERAL RULES FOR USE OF PROTECTIVE MEANS
The personnel carrying out work in electrical installations must be provided with all necessary protective equipment, trained in the rules of use and must use them to ensure the safety of work.
Protective equipment should be kept as inventory in the premises of electrical installations or included in the inventory of mobile teams. Protective equipment may also be issued for individual use.
When working, use only protective equipment marked with the manufacturer, name or type of product and year of manufacture, as well as a test stamp.
Inventory protection means are distributed between objects (electrical installations) and between field crews in accordance with the operation management system, local conditions and manning standards (I will talk about this later).
Such a distribution with an indication of the storage locations of protective equipment should be recorded in the lists approved by the technical manager of the organization or the employee responsible for the electrical equipment.
If the protective equipment is found to be unsuitable, they are subject to withdrawal. The withdrawal of unsuitable protective equipment must be recorded in the log book and the content of protective equipment.or in the online documentation.
Employees who have received protective equipment for individual use are responsible for their correct operation and timely monitoring of their condition.
Insulating electrical protective equipment should be used only for their intended purpose in electrical installations with a voltage not higher than that for which they are designed (maximum permissible operating voltage), in accordance with operating manuals, instructions, passports, etc. for specific means of protection.
Insulating electrical protective equipment is designed for use in closed electrical installations, and in open electrical installations - only in dry weather. They are not allowed to be used in drizzle and precipitation.
Outdoors in wet weather, only specially designed protective equipment designed to work in such conditions may be used. Such protective equipment is manufactured, tested and used in accordance with specifications and instructions.
Before each use of the protective equipment, the personnel must check its serviceability, the absence of external damage and contamination, and also check the expiration date using the stamp.
It is not allowed to use protective equipment that has expired.
When using electrical protective equipment, it is not allowed to touch their working part, as well as the insulating part behind the stop ring or stop.
STORAGE PROCEDURE FOR PROTECTION MEANS
Protective equipment must be stored and transported in conditions that ensure their serviceability and suitability for use, they must be protected from mechanical damage, contamination and moisture.
Protective equipment must be stored in closed rooms.
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials that are in use should be stored in cabinets, on racks, shelves, separately from tools and other protective equipment. They must be protected from the effects of acids, alkalis, oils, gasoline and other destructive substances, as well as from direct exposure to sunlight and heat radiation from heating devices (no closer than 1 m from them).
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials that are in use should not be stored in bulk in bags, boxes, etc.
Protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials in stock must be stored in a dry room at a temperature of (0-30) ° C.
Insulating rods, clamps and voltage indicators above 1000 V should be stored in conditions that prevent them from bending and touching walls.
Respiratory protection equipment must be stored in dry rooms in special bags.
Protective equipment, isolating devices and devices for work under voltage should be kept in a dry, ventilated area.
Protective equipment in the use of field crews or in the personal use of personnel must be stored in boxes, bags or cases separately from other tools.
Protective equipment is placed in specially equipped places, as a rule, at the entrance to the premises, as well as on control panels. Storage areas should have a list of protective equipment. Storage areas should be equipped with hooks or brackets for rods, insulating pliers, portable grounding, safety posters, as well as cabinets, racks, etc. for other means of protection.
ACCOUNTING OF PROTECTION MEANS AND CONTROL OF THEIR CONDITION
All electrical and personal protective equipment in operation must be numbered, with the exception of protective helmets, dielectric carpets, insulating supports, safety posters, protective fences, transfer and potential equalization rods. The use of serial numbers is allowed.
The numbering is set separately for each type of protective equipment, taking into account the adopted system of organization of operation and local conditions.
The inventory number is usually applied directly to the protective paint or embossed on metal parts. It is also possible to apply the number on a special tag attached to the protective equipment.
If the protective equipment consists of several parts, a common number for it must be put on each part.
In the subdivisions of enterprises and organizations, it is necessary to keep logs of accounting and the content of protective equipment.
Protective equipment issued for individual use must also be registered in the journal.
The presence and condition of protective equipment is checked by periodic inspection, which is carried out at least once every 6 months. (for portable groundings - at least once every 3 months) by an employee responsible for their condition, with a record of the inspection results in the log.
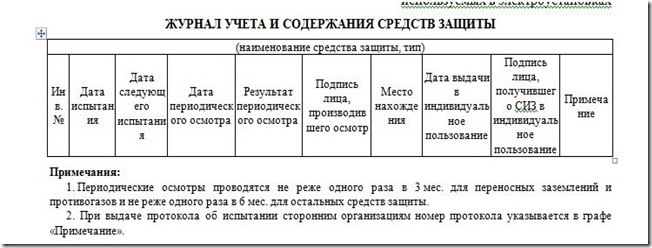
Electrical protective equipment, except for insulating supports, dielectric carpets, portable groundings, protective fences, posters and safety signs, as well as safety harnesses and safety ropes received for operation from manufacturers or from warehouses, must be checked in accordance with the operational test standards.
The protective equipment that has passed the tests, the use of which depends on the voltage of the electrical installation, is stamped with the following form:
Protective equipment, the use of which does not depend on the voltage of the electrical installation (dielectric gloves, galoshes, boots, etc.), is stamped with the following form:
The stamp must be clearly visible. It should be applied with indelible paint or glued to the insulating part near the stop ring of insulating electrical protective equipment and live devices or at the edge of rubber products and guards. If the protective equipment consists of several parts, the stamp is placed on only one part. The method of stamping and its dimensions must not impair the insulation performance of the protective equipment.
When testing dielectric gloves, boots and galoshes, marking should be made according to their protective properties Ev and En, if the factory marking is lost.
On protective equipment that did not pass the test, the stamp must be crossed out with red paint.
Insulated tools, voltage indicators up to 1000 V, as well as safety belts and safety ropes are allowed to be marked with available means.
The results of operational tests of protective equipment are recorded in special journals... Protective equipment owned by third parties should also be subject to test reports..
This concludes today. In the next article, we will begin to consider directly the procedure for testing protective equipment.
I look forward to your questions and see you.
- Rules for the use of electrical protective equipment when carrying out work in electrical installations
- How to sew fleece mittens
- Protective equipment in electrical installations
- Computer glasses: which is better to choose
- How to wash things with Thinsulate insulation
- Training in electrical safety, labor protection, ecology, electrical safety, fire-technical minimum, first aid to victims of the courses
- Protective equipment in electrical installations up to and above 1000 Volts
- What is fleece fabric, where is it used and how to care for it
- Personal protective equipment
- What is this fabric?
- Thinsulate
- Veresaev vikenty vikent'evich
- Vasily Shukshin: Until the third cocks Until the first cocks shukshin
- Svyatogor what he did in the epic
- "Scene with a wounded buffalo"
- VII International Competition "New Fairy Tales" Competition for Writers of Fairy Tales for Adults
- Important organizational points
- Portfolio of the music director of the autonomous preschool institution of the municipality zavodoukovsky urban district "development center
- Awarding of winners and participants of the competition
- D and collect portrait templates