Protective equipment in electrical installations up to and above 1000 Volts
Isolating protective equipment in electrical installations allows the safety of personnel performing maintenance work in existing electrical installations. The main danger of electrical installations lies in the increased likelihood of electric shock and thermal effects of an electric arc.
The type and purpose of electrical protective equipment has a direct impact on ensuring safety against voltage effects. Each electrical protective equipment, depending on its purpose and electrical installation voltage class(up to 1000 Volts or higher) can provide protection for personnel either completely, or used as an additional means of protection.
A significant percentage of accidents in electrical installations occurring annually are due to the fact that workers ignore labor protection requirements, ineptly using protective equipment when working. Knowledge of the correct application of electrical protection measures is invaluable in work involving electrical equipment.
Greetings to all readers of the site " Electrician in the house". Friends in today's article I would like to tell you about what is included in the concept basic and additional means of protection in electrical installations, their list, methods of application and use.
What means of protection are used in electrical installations
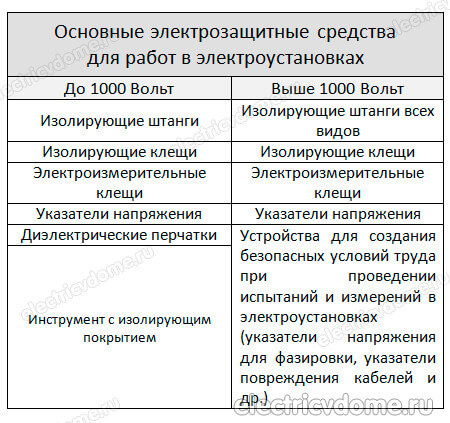
In the course of work in electrical installations, regardless of which section or subdivision they belong to, the maintenance personnel must apply various protective measures to prevent electric shock. Any electrical protective equipment is divided into two types: basic and additional. What is their difference?
Basic means of protection in electrical installations withstand voltage for a long working time and are used in the course of work when the equipment does not need to be disconnected from the mains. That is, an employee, using the main means of protection, can safely work on equipment, the live parts of which are energized.
Additional means of protection in electrical installations cannot serve as 100% protection for personnel from electric shock, it is used in conjunction with fixed assets.
I present a screen of how the word-for-word definition sounds and what is the "main and additional" protective means according to the rules.


The essence of the means for electrical protection in electrical installations with voltages up to and above 1000 Volts and the requirements for them should be discussed in more detail.
Basic means of protection
For a more accessible perception of information, you should consider in more detail up to and above 1 kV and their scope. So, the set includes basic and additional protection means in electrical installations.
Let's take a closer look at what each of them is intended for.
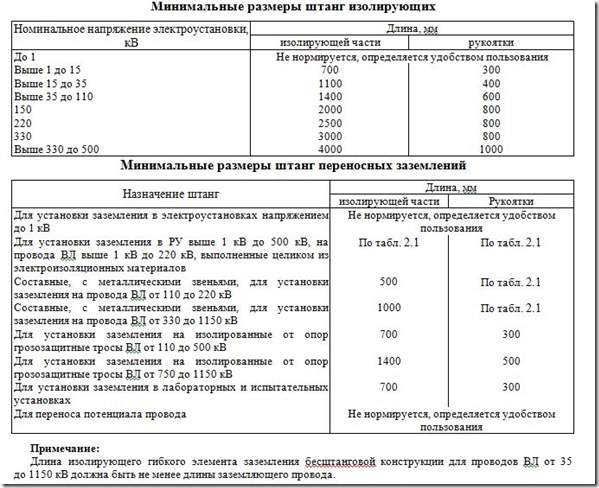
1. Insulating rods
The designs of the insulating rods are different and allow you to install protective portable grounding, perform operations with switching devices, install insulation pads, change fuses, measure and release victims in case of electric shock.
Before using the boom, make sure it is designed for the operation. It is forbidden to perform work with the barbell for which it is not intended.
2. Insulating pliers
This type of protective equipment successfully allows replacing fuses and removing insulating linings, protective shields, etc. When replacing fuses, the voltage class of which is more than 1000 V, in addition to insulating pliers, dielectric gloves, masks or goggles should also be used. It is possible to replace fuses in electrical installations up to 1000 V using pliers or dielectric gloves using glasses or masks.
3. Electric clamp
Everything should be clear here; these clamps are needed for measuring electric current. There can be both narrow-profile ones that allow you to measure only the magnitude of the electric current, and universal (modern) ones with which you can also measure the voltage and resistance of the circuit. The first category includes tools above 1 kV.
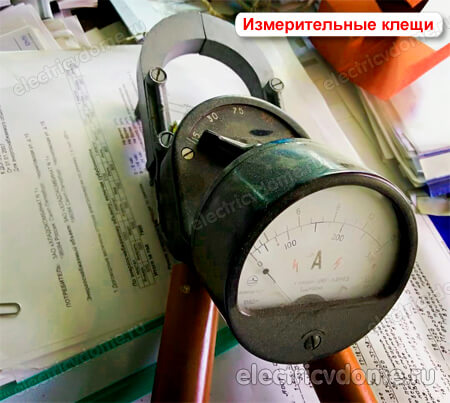
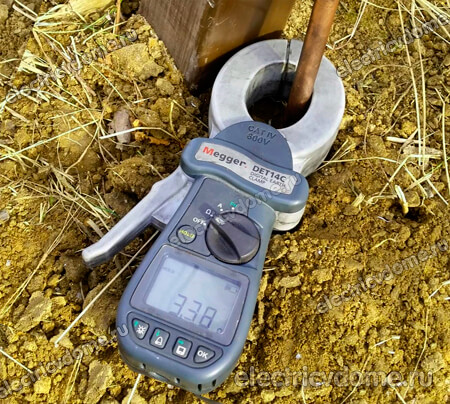



This type of clamp effectively measures the load of the network, the power of devices, allows you to check the electricity meters and determines the parameters of the network. In electrical installations above 1 kV, such a tool is designed for voltages up to 10 kV inclusive.
4. Voltage indicators
With the help of voltage indicators, the absence or presence of voltage on live parts of the equipment is checked.
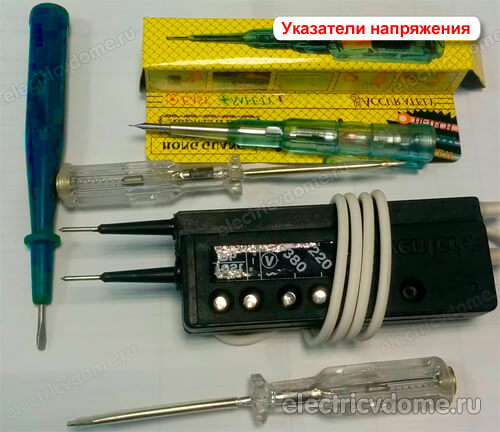

If it is necessary to check whether there is voltage on live parts, a preliminary check of the operability of the voltage indicator itself is necessary. This check is carried out on live parts of switchgear type devices under operating voltage. You can check the performance of voltage indicators over 1000 V using special devices that are designed to test indicators.
5. Dielectric gloves
In electrical installations of different voltage classes, dielectric gloves can be used as the main and additional means of protection. In electrical installations with voltages below 1000 volts dielectric gloves are the main means of protection, in electrical installations above 1000 Volts - additional.

Dielectric gloves are used by employees only when dry. If the humidity in the room exceeds the norm, the gloves should be completely dry at room temperature by the time of use.
By the time of operation of these products, they should be visually inspected, check the date of the next tests and the absence of punctures. In order to detect punctures, gloves should be rolled from the edges towards the fingers. The glove is inflated, and then potential punctures for the release of air are detected by pressure.
6. Tool with insulating handles
This category includes all hand tools equipped with insulating handles (various pliers, screwdrivers, wrenches, etc.) used as fixed assets for electrical protection if electrical work is performed in electrical installations up to 1000 V that do not require stress relief. This tool is a fitting and assembly tool used for connecting and repairing electrical installations, the voltage of which is up to 380 volts.

In electrical installations over 1000 V a tool with an insulating handle is not completely safe during work.
If an electrician performs work on equipment up to 1000 Volts without removing the voltage, one tool equipped with insulating handles will not be enough. Insulate the employee from the ground or floor using dielectric rugs, insulation stands, or dielectric footwear. Protective equipment (goggles, masks) are selected depending on the nature of the work.


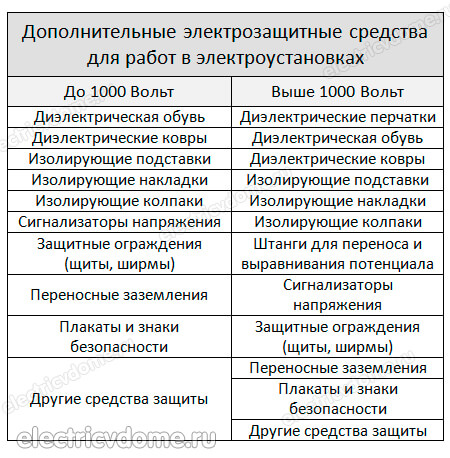
The above are basic and provide electrical protection when performing work in electrical installations up to and above 1000 V. Next, you should talk about what the list of additional protection means represents a failure.
Additional means of protection
In the course of work in electrical installations up to 1 kV, it is enough to use one additional tool.
1. Dielectric shoes - boots, galoshes
The purpose of dielectric boats or galoshes is to protect people from electric shock who close to the ground in the area of action of step voltage.
Dielectric shoes provide excellent protection when people need to be insulated from the ground or conductive floor in the room, as shoes serve as an alternative to dielectric rubber carpet or insulating pad.


Before using the products, a thorough inspection of dielectric shoes is carried out so that there are no punctures and noticeable damage in it. The dielectric footwear used requires careful movement, punctures are not allowed. This is doubly true for open areas. If the surface of dielectric shoes is damaged, a person could suffer from a sudden electric shock, such as being in the area of a step voltage.


Before using bots or galoshes for work, be sure to check the stamp with the date of further tests. An equally important indicator is the voltage at which insulating shoes will reliably protect a person from the effects of current.
2. Dielectric rugs and tracks
The purpose of these products is similar to dielectric shoes. They are used as additional electrical protective equipment in installations up to and more than 1000 V. Carpets can be used in closed-type electrical installations, with the exception of damp rooms, and in open-type electrical installations in dry weather.

3. Insulating feet
Designed to prevent direct human contact with the floor. They are wooden gratings with reinforcements on insulators made of porcelain and plastic. If the voltage is not more than 1 kV, electrical protective supports are used that are not equipped with porcelain insulators.
4. Insulating caps
Insulating caps are used in electrical installations up to 10 kV, structurally, in accordance with the conditions of electrical safety, excluding the possibility of imposing portable groundings, if repairs, tests are carried out, the place of damage is determined.
The installation of these components occurs on the conductors of cables that are disconnected and located not far from live parts, under operating voltage, at the poles of disconnectors, etc.
5. Voltage alarms
To ensure additional safety when performing work in electrical installations over 1000 V, voltage alarms are used.
An employee's wrist or helmet is used to attach the voltage alarms. A reaction occurs when a person approaches energized parts. The signaling device reacts to magnetic fields and emits sound and light signaling.
Voltage alarms are an additional means of protection. Based on its readings, it is impossible to judge the absence of voltage on the equipment. The absence of voltage MANDATORY must be confirmed using a voltage indicator.
6. Bars for leveling and potential transfer
They are used to transfer the potential of overhead lines to the workplace of an electrician and equalize the potential between an individual shielding set and large-sized devices with a variable potential value.
7. Portable protective earthing
So that a person does not suffer from accidentally applied voltage and the induced voltage of individual transmission lines does not affect him, they resort to equipment grounding. For this, live parts are connected to the ground loop. Equipment is grounded using two types of grounding: stationary and portable.
Stationary grounding knives are located directly on the equipment body and are its structural component. For example, earthing knives on disconnectors.
Portable grounding must be installed manually, this is done using removable or stationary insulating rods (located on the PP themselves).

Accidents that occur due to the fact that the voltage at the time of installation of grounding on all 3 phases has not been checked, occur more and more often. Switching devices, with the help of which a section of equipment is turned off and a visible gap is created, are turned off half-phase. One phase remaining energized is enough for a person to be electrocuted when installing the ground.
When installing portable grounding on equipment with voltages above 1000 V, in order to ensure safety, insulating rods and dielectric gloves must be used.
In order for portable grounding as a means of additional protection to provide protective functions, it is necessary to correctly select its type and section based on the voltage class and operating currents that occur in the area of the electrical installation where the grounding should be installed.
In addition to the above means, the use of personal protective equipment in the form of special clothing, shoes and helmets is justified. Based on the terrain conditions and the nature of the work, it is necessary to use protective equipment against the effects of negative factors.
Protective clothing must be worn in an area characterized by an increased influence of the electromagnetic field. On-line switching uses a protective suit and a visor to protect against potential arc effects.
The main rules for the use of electrical protection means, relating to all means of protection, without exception, are manifested in the following.
When working with protective equipment, the degree of suitability for use is first checked. The decisive factor is the appearance of the insulation product. The presence of a damaged body, cracks and contamination of the paintwork is not allowed.
Any insulating protection means in electrical installations are tested in a specified period with a test for operational suitability in electrical installations. By the time the protective equipment is applied, its validity period is checked with the date of further tests. The date should be stamped.
If there is dirt, damage to the case or overdue test period on protective equipment, the product is not used due to the likelihood of electric shock. Removal of protective equipment from operation is carried out, allowing troubleshooting and testing.
- Rules for the use of electrical protective equipment when carrying out work in electrical installations
- How to sew fleece mittens
- Protective equipment in electrical installations
- Computer glasses: which is better to choose
- How to wash clothes with Thinsulate insulation
- Training in electrical safety, labor protection, ecology, electrical safety, fire-technical minimum, first aid to victims of the courses
- Protective equipment in electrical installations up to and above 1000 Volts
- What is fleece fabric, where is it used and how to care for it
- Personal protective equipment
- What is this fabric?
- Thinsulate
- That even the pants ran away. History of creation. Stolen sun - Chukovsky K.I
- Yegor creed and dasha klyukina meet or not after the bachelor project it is interesting to all fans of the television show Bachelor 2 to know how the relationship developed
- The Five Winners of The Voice: What Are They Doing Now?
- How much does it cost to participate in a talk show on Channel One “Let them talk
- Andrey Malakhov revealed the true reasons for leaving the first channel
- Jealous Pavel Volya made a loud scandal for Lyaysan Utyasheva right on the set of the show Is it true that Volya and Utyasheva are getting divorced
- Life of Amiran Sardarov from Khach's diary
- X Y Z - theory of generations Generations x y z search for dialogue essays
- Khovansky versus Afoni: how an alcoholic of a major exposed from what city Khovansky